The Cost of Perceived Wisdom: why we really don’t like innovation
 In 1996 my sister called to say she’d made an online purchase. I was surprised: in those early days it was not only difficult to search for anything on the new internet, there wasn’t much to search for. Certainly, purchasing anything seemed illogical – we had no way of knowing if ‘secure lines’ were, well, secure. Curious, I asked my sister to explain her decision process.
In 1996 my sister called to say she’d made an online purchase. I was surprised: in those early days it was not only difficult to search for anything on the new internet, there wasn’t much to search for. Certainly, purchasing anything seemed illogical – we had no way of knowing if ‘secure lines’ were, well, secure. Curious, I asked my sister to explain her decision process.
J: I needed a simple Y connector, and decided to see what online purchasing was all about. This was my test case. I found three companies with the exact same product at the same price.
SD: How did you choose which company to buy from?
J: Since the price and products were identical, I decided I’d trust the company with the best customer service so I’d be cared for if I had a problem. Because none of the websites mentioned customer service, I decided to call them and ask. The first company kept me on hold for 23 minutes before I hung up. The second call put me straight through to a voice message. A sales rep answered my call in the third company, asking me if I had questions. So it was an obvious choice. There was only one company that took care of me.
I then realized there were three problems with the current (1996) search capability:
- Site visitors had only a haphazard method of finding what they wanted;
- People had no way to identify their unconscious criteria for resolving their query, even if they could find what they initially thought they wanted;
- Sites could only meet the search criteria imagined by the site designers, sometimes overlooking criteria sought by visitors.
In other words, if people were happy with the information they were able to find on a site, they were satisfied. For those folks not entirely clear what they needed, couldn’t find the page matching their search criteria, or had needs outside the obvious, there was a probability they couldn’t find what they really needed and would leave the site.
MY SEARCH INVENTION DEFIED THE NORM
I decided to create a tool to help site visitors become aware of the unconscious criteria (i.e. not just the information, but the intuitive essential criteria they needed met) they needed and be led directly to the page(s) that offered the exact answers they sought. And in 1996, no one else was thinking this way.
Enter Hobbes. With a few sequenced Facilitated Questions (a new form of question I invented that helps people find their unconscious criteria where they make decisions), a simple backend tree, and carefully culled choices of criteria-based options, my search tool Hobbes would help site visitors discover their real decision making criteria and lead them directly to the one or two site pages that met their needs.
For those who chose to use Hobbes, this would keep them on the site and help them become buyers or satisfied visitors. It would also cause companies to do their homework to learn what visitors truly needed and add those responses to their sites.
Of course, this was way outside of conventional practice, especially almost 30 years ago – 3 years before Google search came out. Yet 54% of site visitors on my site used it.
I tried to get funding for it and was offered $15,000,000 by the only woman VC in Silicon Valley IF I could find $1,000,000 from someone else (a man). Nope. Only 0.25% of women were receiving funding in those days. (Today, 30 years later, it’s ballooned up to 2% but who’s counting.)
Sadly, I kept hearing that no one needed a search tool for ‘criteria’. Silly idea, I was told countless times, no one makes decisions from criteria. And yet, as we now know, we all do. In fact, the time it takes us all to discover our criteria is the length time it takes to make a decision.
The concept died. No one wanted a search capability that enabled a site visitor to directly find what they needed on a site.
PERCEIVED WISDOM REIGNS
You all know what happened next. Google search entered and the rest is history. But in 2010 one of the leaders at Bing called saying they’d heard about Hobbes and could they buy it. I shared the original site design. Yay! ‘Love it. We could start using this immediately! What a great idea to help people uncover their unconscious criteria and help them find what they need quicker.’
But he called back the next day: the team hated the concept. ‘Why would anyone want to use a search tool that doesn’t seek out information like Google does?’ It was the accepted norm and ‘no one would want to do anything different’.
And so the perceived wisdom has prevailed through decades. Imagine if we had choices.
WHO AM I? AND WHY DOES CRITERIA MATTER?
I invent systemic brain change models that enable people to get to the specific circuits in their brain that holds their decision making criteria, used to help people buy(Buying Facilitation®), learn (Learning Facilitation), Change (Change Facilitation), etc. And as with Hobbes, because they go against perceived wisdom, most folks are unwilling to adopt them even when they prove, in controlled studies with major corporations, in following the 100,000 folks I’ve trained them to, to be more successful than the standard models.
Success, it seems, is not the criteria. Innovations – as wonderful as they’re made out to be – are not accepted readily: they buck the system, go against the norm.
WHAT IS PERCEIVED WISDOM AND WHY DOES IT MATTER?
My Hobbes story provides a background for my grumble about innovation: normalized thinking limits our worlds, rules our assumptions and restricts creativity.
I’ll begin with my definition of perceived wisdom (PW). PW is another way of saying ‘the norm’, the accepted myths, practices, ideas that constitute the immediate assumptions we make without questioning them. It’s the accepted convention, the ideas we’ve used to set up our lives, our thinking, our work environment and expected behaviors.
PW is perpetuated in every sphere of our lives; it permeates our education, cultures, religions, what we buy and wear, who we marry and where we live.
Our thinking, our behaviors are often based on accepted norms that have become ubiquitous: * Do you avoid white after Labor Day? (Silly) * Do you feed a cold and starve a fever? (Wrong) * Calories-in determines weight (proven false). * Behavior Modification works to help you lose weight, exercise, change habits, yadayada. (There’s no scientific evidence anywhere that it does, it has a 97% fail rate, and you can’t change a behavior by trying to change a behavior). I once asked my mother if she nursed me. ‘I would have, but everyone said it would harm you. And now I’m sad about it.’
PW meets our foundational criteria of belonging: it offers comfort, safety, absence of uncertainty, and no risk of encountering scorn or derision. And because PW is aimed toward the middle of the road (where, according to the late, great, Molly Ivins, only yellow stripes and dead armadillos exist), we spend our lives unwittingly maintaining and recreating a specious status quo that causes us to lose our uniqueness. Our language, our conventional assumptions, keep us like gerbils, going round and round the same ideas and conventions regardless of their success or failure. So
- in sales, a 5% success rate is acceptable, and the matching 95% failure rate is not even mentioned – folded in to the costs as a ‘given’ because the model itself is flawed and hasn’t been reconceived in a century;
- in leadership and coaching, the assumption that the person ‘in charge’ has the knowledge that Others must conform to, and their resistance is something to be managed, resulting in a 97% failure rate;
- in training, the information-in approach doesn’t integrate with brains and causes a 90% fail-to-retain rate (here’s my Learning Facilitation model that enables permanent retention).
Even great Harvard thinkers like Chris Argyris and Howard Gardner have written books on managing resistance, using the baseline PW assumption that all change involves resistance. Nonsense. Another faulty fact we’ve normalized and have cost us dearly. It’s certainly possible to enable people to change from their core criteria instead of the biased questions and rules created by leadership.
While we think our personal beliefs are specific to us, they are invaded by the PW in the customs we live in. It’s where we get our racial biases, our assumptions about education, class, age, history. We’re so hamstrung by PW we’ve become tribes, where our politics and beliefs keep our ‘team’ on the good side and we hate everyone else, like sports fans.
And since it’s endemic we find no reason to reject it, even going so far as passing down these baseless concepts through generations and unquestioningly resisting anything that’s different.
But worst of all, it restricts our creativity. Indeed, from health, to sex, to climate change and politics and relationships, almost every area of life is circumscribed by PW. It’s pernicious.
THE PERCEIVED WISDOM OF CURRENT SEARCH CAPABILITY
How PW restricts our worlds is a huge topic, involving our health and healthcare system, our financial system, the environment, education, privacy – the list goes on. But because the topic is so important, I’m going to show you how limited we are in one sector – internet search – and how our worlds get shoved into tiny vessels of biased, restricted information as a result.
It didn’t start out that way, but we don’t even notice. Most of our online interactions are now suspect: even simple searches lead us to knowledge selected by algorithms that restrict us to the demographic we’ve been thrust into, causing facts to seem like fake news.
Our use of Google as a search engine is ubiquitous. This company determines what we read and the information we have access to. Even scientific facts are suspect as they’re fed to us according to where we live, who we vote for, what we read.
And here’s the worst part. Google’s standard monetizing procedures, as to all search capabilities, tag us into a demographic and sells our personal data to thousands of advertisers who spam us. Rarely do we find the full range of possible solutions, answers, or ideas. I recently was led to a site that seemingly had the data I needed only to receive a phone call WHILE I WAS STILL LOOKING AT THE SITE from a sales person FROM THAT SITE who wanted to sell me something!
Surely we should care about accurately nourishing our curiosity without fear of spam and Robo calls.
THE MISSING VOICE ON THE INTERNET
One other aspect of PW bugs the hell out of me, and that might supply answers to my ‘whys’: Have you realized that men – the male human of our species – designed, developed, and generated the internet and social media – and continue to do so? The PW is the male view of the internet; we use it (and it abuses us) by the requirements, the criteria, of men. And we all buy into it.
How different would it be if women’s voices and ideas – currently a tiny fraction of the design of the internet – had been involved in the creation of our technology? Has the male viewpoint become so much a part of our culture that we all just assume that’s the way it is and should be (PW), and never stop to consider the results if women played their representative percentage in designing it?
Seriously: how would the internet or social media be different if it had been designed by women? Or designed by 50% women? Or designed in equal measure by people of color, people from different cultures, people of different levels of education. We’ll never know. What we do know is that the internet is the Perceived Wisdom of White Men in Silicon Valley. And we’ve normalized it as being The Way It Is.
WHY GO BEYOND PERCEIVED WISDOM?
Of course, going outside the box is hazardous. But disputing PW is vital:
- Obviously, there’s nothing in the middle of the road except yellow lines and dead armadillos. Who would want to be there anyway?
- New ideas can’t come from the middle. New ideas always come from the ends.
- There’s no debate, curiosity, creativity, free expression in Perceived Wisdom.
- Things change. Time, ideas, technology culture. Wisdom must change too or we stagnate.
- Perceived wisdom is linear. Real life occurs in systems.
- Perceived wisdom is what u get when everything is thrown into the middle and becomes moderate enough to please most. Vanilla.
New ideas come from that small percent outside the mainstream, with innovative ideas that are loud enough, insistent enough, and interesting enough to push into the middle, eventually change, and become part of, the PW. But getting there – the journey – is the creative part. And those of us willing to take on the job must have very tough skins. Instead of our criteria being comfort, we must shift our criteria to truth and integrity, collaboration and serving.
What, exactly, is so powerful about perceived wisdom that whole industries (healthcare, sales, coaching, leadership) prefer to suffer failed strategies rather than add anything new to ensure success? What would we need to believe differently to be willing to question our long held assumptions? How can we tell if a long held assumption is wrong, or incomplete, or could be expanded, or worth thinking of something different? And how would each of us need to be different to be willing to hear fresh ideas and new voices that seemingly conflict with all we think we hold dear?
The good bit is that going against the norm is fabulous. As an inventor of systemic change models that work with criteria instead of information, I’ve been doing it for many decades, and the rewards make up for the pitfalls. I urge anyone with original ideas, passion for truth, and a hunger for diversity, creativity, and integrity, to shout that the perceived wisdom is wrong, and put forth
- Diversity of ideas,
- Fresh ideas from different cultures, ethnicity, countries, educational backgrounds,
- True creative thinking that pushes industries (sales, coaching, leadership, listening, change) to new vocabulary and (slowly slowly) new thinking,
- Expanded possibilities for innovation,
- Ideas that inspire other ideas that wouldn’t have otherwise been stimulated.
If our criteria is for better, more authentic ideas, for equality and integrity, we must go outside PW where innovation comes from. PW is merely the group/tribe acceptance of the status quo that has been standardized by the masses. Let’s all be innovators; let’s all shout out new truths and challenge the norm. And let’s all listen to the dissenters because they may be shedding light on new truths.
Our perceived wisdom is faulty. And until we begin thinking differently and stop acting as if PW is true, it cannot change and we will not readily accept innovation.
Let’s discuss this. I’m happy to discuss should anyone want to contact me. Sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com or 512 771 1117.
______________________________________
Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen September 29th, 2025
Posted In: Communication, News
50% of Sales Professionals are Neurodiverse: An introduction to finding, hiring and retaining them, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 In 1979, with a toddler to feed on a social worker’s salary of $19,500 annually, I decided to ‘go into business’ (whatever that meant) to earn more money. I went to Goodwill, bought a ‘business’ dress for $12.00 and took myself to Wall Street, thinking that was where I would find ‘business’.
In 1979, with a toddler to feed on a social worker’s salary of $19,500 annually, I decided to ‘go into business’ (whatever that meant) to earn more money. I went to Goodwill, bought a ‘business’ dress for $12.00 and took myself to Wall Street, thinking that was where I would find ‘business’.
Not knowing the protocol I walked into Merrill Lynch, White Weld International on 1 Wall Street. ‘Who’s in charge of hiring people?’ I naively asked a receptionist. ‘You need the CEO. Go up to the 50th floor,’ she said and pointed to a tiny (four person) elevator.
On the 50th floor I was greeted by a secretary who asked who I was there to see. ‘The CEO’. She smiled, then walked me into his office. The CEO of Merrill Lynch got up from his enormous desk in a windows-filled, corner office overlooking Battery Park and walked over to greet me. ‘How can I help?’ he asked this brazen young woman who’d just pranced in unannounced in a cheap dress. ‘I want you to hire me.’ He laughed.
CEO: What can I hire you as?
SD: A trainer.
CEO: Let’s make you a stockbroker.
SD: But I know nothing about stocks or bonds. (How I thought I was going to train anything is a mystery!)
CEO: If you could do what you just did, I’ll not only hire you, I’ll train you myself.
And he did.
It was a bear market. The Dow was 777 (Really!) and the brokers were suffering. But once I got trained, I was closing new clients daily. I would cold call people by saying: “Hi. My name is Sharon-Drew Morgen. I’m a broker at Merrill Lynch. This is a cold call. I want to be your broker, and I will most likely lose your money, but I’ll sure try not to.” ‘Oh!’ said the prospects. ‘An honest broker! Everyone else is losing me money and lying to me about it!’ I closed almost every prospect I called and became the rookie of the year.
Looking back, I unwittingly used unconventional standards to get my first job in business. I didn’t know any better: I have Asperger’s Syndrome, on the Autism Spectrum. As a social worker before that, I had no way of knowing I wasn’t supposed to walk into someone’s office (especially the CEO of Merrill Lynch!) and tell them to hire me; I didn’t know I wasn’t supposed to tell people I would lose their money. As an Aspie I’m honest and direct. And very authentic. I was just telling people the truth. I ended up making a ton of money as a result. And yes, I lost everyone’s money.
No one knew what a neurodiverse person was in those days, nor did they care. My invisible ‘disability’ gave me the precise skills I needed to be a successful sales professional: relentlessness, hyperfocus, trustworthiness and authenticity, attention to detail, creativity, loyalty, and honesty. My most relevant skill for the job was my comfort with being rejected. With Asperger’s, I was accustomed to navigating adversity. Being neurodivergent made me successful.
NEURODIVERSITY IN SALES
Twenty percent of the workforce, and 50% of sales professionals are neurodivergent. In other words, of the 40,000,000 sales professionals worldwide, 20,000,000 are neurodivergent. And 75% of these people are undisclosed due to their fear of facing discrimination.
For some reason, while hiring folks of different races and gender orientations are standard, many companies avoid hiring neurodivergent (ND) people. But why? Sure, we’re different. Aren’t we all? What is it about neurodivergence that causes neurotypicals (NTs) to avoid us?
Thankfully, undisclosed ND people who can cope with standard hiring practices are being hired. But certainly, we’re not being interviewed in a way that makes getting a job easier and, once hired, we receive no services that help us flourish.
As a result, we face discrimination, get relegated to jobs well below our intelligence, and get shunned by colleagues and at meetings. I personally found myself in trouble often for doing things I didn’t know I shouldn’t do. Having a mentor or manager who could help me navigate NT standards would have made my job so much easier and helped me be even more successful. Instead of the stress of fitting in falling on my shoulders, I could have had an easier path to acceptance and acculturation.
CULTURE OF INCLUSION
Creating a culture in which ND employees not only fit in but are active, accepted members of the community, takes work. It’s not merely doing a few things differently but having a commitment to an inclusive workplace where everyone thrives, welcomes diversity, and collaborates. It means a culture change.
Company culture
Having a culture of inclusivity makes it easier to hire and retain ND sales folks. When you advertise your company as a culture of inclusion, the people who get hired are expected to respect and include everyone, regardless of race, gender, or neurodiversity. This gives ND folks the green light to apply for a job.
Since the focus of this article is on hiring and retention practices (below), I’ll just mention a few areas to address to make sure you’ve got an inclusive culture;
- Publish corporate guidelines on inclusion in all written communiques so both the public and current employees are aware.
- Rethink hiring practices to provide interviewing choices that help NDs interview comfortably.
- Discover the barriers to inclusion within the company and begin the process of unblocking them.
- Provide management training to give managers specific skills for communicating with, and helping NDs fit in.
Once the company culture is set up for inclusion, you’ll need to know the specifics for hiring and retaining ND employees.
Hiring practices
Neurodivergent salespeople are wonderful, loyal, successful employees who can give you a competitive advantage, but require different competencies to hire: We don’t make small talk and prefer plain-spoken questions; may not make direct eye contact; and may not answer typical interviewing questions in ways the interviewer is familiar with. Obviously not great for door-to-door sales but terrific for technical sales, e-commerce sales, cold calls, and business development research. We also make great account managers: our long term clients love us because of our truth telling, attention to detail, and loyalty.
Our different competences require a different interview process than hiring NT employees and may be best served with either email or zoom interviews. With a job spec that includes a sentence like Those applicants who need specific hiring accommodations, please tell us what you need, the applicant will provide the interviewer the specifics of an interview format to get the best interview possible. Remember: we’re different; standard norms will need to shift.
Retaining neurodiverse salespeople
Here are some ideas for managing and retaining neurodiverse sellers:
- For ND sellers working in a corporate building (and many work best from a home office) offer them a workspace situated away from lights or noise. Having a ‘quiet room’ on the premises helps.
- Make sure necessary information is in visual and written formats.
- Make sure we know how and when to use the appropriate technology. A ND techie (50% of tech folks are neurodivergent.) makes a great mentor!
- Managers must have appropriate communication skills as communication is quite different with ND folks. We may understand differently but are delighted to be told we’re doing something wrong and shown the right way. And note: consider bringing in an outside company to help here, like Ochtivate.
- Send out general questionnaires (no names required) that seek data from all sales folks with a specific note for undisclosed NDs to make requests, complain, etc. There’s no other way to get to the undisclosed ND population to provide any help they might need.
These are a few of the things that will help retain the ND sales professional; there are many books on the market that go into detail.
As I end this article, I’ll share something I do that works well most of the time to inoculate me from my communication partner’s assumptions of how I communicate. Indeed, I have found grace and kindness when I tell prospects/clients:
- “I have Asperger’s. That means I’m a bit loquacious, obnoxious, and annoying. But I’m also committed to using my knowledge, creativity, commitment, and integrity to serve you. So if you can put up with the annoying stuff, I am here for you.”
This has gotten me more business than any pitch or price reduction could have. And it’s absolutely honest.
Net net: the neurodiverse sales professional is eager to work hard, and can be your most loyal, successful seller. But make sure they have the right tools, in an accepting environment, with appropriate managers and mentors. We’re just different. But aren’t we all?
If you’d like some coaching to set up a culture of inclusion, or facilitate hiring and success practices for neurodiverse sales professionals, call me and we can discuss. sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com
_______________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen September 22nd, 2025
Posted In: Sales
Influencing Congruent, Unbiased Change: serving with integrity, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
As influencers we aim to help Others achieve their own brand of excellence, using their own unique values and standards. Sadly, too many of us – coaches, leaders, sellers, consultants, doctors, parents – try to get Others to accede to our viewpoints and suggestions, believing we have information or solutions that offer ‘better’ choices than the ones they’ve made. We’re telling them, net, net, that we’re smarter, that we think our ideas are better than their own.
It’s not our intent, but due to the way we engage with others, and the way brains work, we inadvertently end up restricting possibility and creating resistance, conflict, antagonism, or disregard, regardless of the efficacy of what we have to offer.
In this article I’ll explain how we end up creating the very resistance we prefer to avoid, and introduce new skills to enable us to truly serve.
WE CONNECT THROUGH OUR OWN SUBJECTIVITY
Regardless of the situation, when we try to effect change using our own viewpoint or beliefs (even if they are valid), our unconscious biases and expectations cause us to inadvertently alienate those who might need us. As a result, we ultimately influence only a percentage of those who need our help – those who already basically agree with us.
I’ll explain, below, how we restrict our interactions and then offer new ways to approach influencing to enable others to find their own best solutions:
Biased listening: We each listen to Others unconsciously, through our brain’s unique and subjective filters (biases, triggers, assumptions, habitual neural pathways, memory channels), regardless of our concerted attempts to accurately hear what’s intended. As a result, what we think we hear is often an inaccurate translation of what was meant and not what the speaker intended.
So our Communication Partner (CP) might say ABC but we actually ‘hear’ ABD (And yes, we often hear something quite different than what was said although it shows up as ‘real’. Read my article on how this happens.) and our brains don’t tell us we’re misunderstanding. Unfortunately, it works both ways and Others also wittingly misconstrue what we’ve said.
I wasn’t fully aware of the extent of this until I researched my book What? Did you really say what I think I heard? on how to hear others without bias. With the best will in the world we end up only accurately hearing, and thereby responding to, some percentage of the message our CPs intend. It’s outside of our conscious awareness. But it’s possible to remedy by listening with a different part of our brain. More on this later.
Fact #1. We hear Others through our subjective biases, assumptions, triggers, habituated neural pathways, and beliefs, causing us to unintentionally misinterpret the message intended, with no knowledge that what we think we’ve heard is mistaken. Obviously this effects both sides of a communication (i.e. Speakers and Listeners).
Subjective expectations: We enter into each conversation with expectations or goals (conscious or unconscious), often missing avenues of further exploration.
Fact #2. Entering conversations with very specific and self-oriented goals or expectations (conscious or unconscious) unwittingly limits the outcome and full range of possibility, and impedes discovery, data gathering, and creativity.
Restricted curiosity: Curiosity is both triggered and restricted by what we already know, i.e. you can’t ask or be curious about something you have no familiarity with to begin with. Using our own goals to pose questions that are often biased, assumptive, leading, etc. we inadvertently reduce outcomes to the biases we entered the conversation with; our subjective associations, experiences, and internal references restrict our ability to recognize accurate fact patterns during data gathering or analysis.
Fact #3: We enable Others’ excellence, and our own needs for accurate data, to the extent we can overcome our own unconscious biases that restrict the range and focus of our curiosity.
Cognitive dissonance: When the content we share – ideas, information, advice, written material – goes against our CPs conscious or unconscious beliefs, we cause resistance regardless of the efficacy of the information. This is why relevant solutions in sales, marketing, coaching, implementations, doctor’s recommendations etc. often fall on deaf ears. We sometimes unwittingly cause the very resistance we seek to avoid when we attempt to place perfectly good data into someone’s idiosyncratic, habituated belief system that runs different to our own.
Fact #4. Information doesn’t teach Others how to change behaviors; behavior change must first be initiated from beliefs, which in turn initiates buy-in.
Systems congruence: Individuals and groups think, behave, and decide from a habitual system of unconscious beliefs and rules, history and experience, that creates and maintains their status quo. We know from Systems Theory that it’s impossible to change only one piece of a system without effecting the whole. When we attempt to offer suggestions that run counter to the Other’s normalized system, we cause Others to risk incongruence and internal disruption. Hence, resistance.
Unfortunately for those of us trying to effect change in Others, it’s important to remember we’re outsiders: as such, we can never fully comprehend the ramifications of adding our new ideas, especially when every group, every person, believes it’s functioning well and their choices are normalized and habituated.
Just because it seems right to us doesn’t mean it’s right for another. Sometimes maintaining the status quo is the right thing to do for reasons we can’t understand; sometimes change can occur only when internal things need to shift in ways we cannot assist with.
Net net, we pose questions biased by our own need to know, offer information and solutions that we want to be adopted/accepted, and focus on reaching a goal we want to reach, all of which cause resistance: without buy-in and a clear route to manage any fallout from the potential change that a new element would cause (regardless of the outsider’s belief that change is necessary), congruent change can’t occur. When the ‘cost’ of the change is more than the ‘cost’ of the status quo, people will maintain the status quo.
Fact #5: Change cannot happen until there appropriate buy-in from all elements that will be touched by the change and there is a defined route to manage any disruption the change would entail.
Due to our standard questions and listening skills and assumptions that our terrific information will help, we end up helping only those few whose brains are set up to change (the low hanging fruit) and failing with those who might need us but aren’t quite ready.
INFORMATION DOESN’T FACILITATE CHANGE
We can, however, shift from having the answers to helping others achieve their own type of excellence (regardless of whether or not it shows up looking like we envisioned). In other words, we can help our CPs change themselves. Indeed, by thinking we have the answers, by driving our own outcomes, we lose the opportunity to serve, enable real change, and make a difference.
Don’t take the need to maintain the status quo lightly. Even patients who sign up for prevention programs have a history of non-compliance: with new food plans, or recommendations of exercise programs that challenge the behaviors they have habituated and normalized (for good or bad), they don’t know how to remain congruent if they were to change. (Note: as long as healthcare professionals continue to push behavior change rather than facilitate belief change first, non-compliance will continue.)
It’s possible to facilitate the journey through our CPs own hierarchy of values and rules, enable buy-in and agreeable change, and avoid resistance – but not by using conventional information gathering/sharing, or listening practices as they all entail bias that will touch only those with the same biases.
To enable expanded and managed choice and to avoid resistance, we must first help Others recognize how to congruently change their own status quo. They may have buy-in issues or resource issues; maybe their hierarchy of values or goals would need to shift, or their rules.
By focusing on facilitating choice/change first we can teach Others to achieve their own congruent change and then tailor our solutions and presentations to fit. Otherwise, our great content will only connect with those folks who already mirror the incoming data and overlook those who might have been able to change if they had known how to do so congruently.
THE SKILLS OF CHANGE
I’ve developed a generic Change Facilitation model, often used in sales (Buying Facilitation®) and coaching, that offers the ability to facilitate change at the core of where our status quo originates – our internal, idiosyncratic, and habituated rules and beliefs.
Developed over 50 years, I’ve coded my own Asperger’s systemizing brain, refitted some of the constructs of NLP, coded the system and sequence of change, and applied some of the research in brain sciences to determine where, if, and how new choices fit.
Using it, Others can consciously self-cue – normally an unconscious process – to enable them to discover their own needs for change in the area I can serve, and in a way that’s congruent with the rules and beliefs that keep their status quo in place.
I’ve trained the model globally over the past 30 years in sales, negotiation, marketing, patient relationships, leadership, coaching, etc. Below I introduce the main skills I’ve developed to enable change and choice – for me, the real kindness and integrity we have to offer.
It’s possible to lead Others through
- an examination of their unconscious beliefs and established systems
- to discover blocks, incongruences, and endemic obstructions
- to examine how, if, why, when they might need to change, and then
- help them set up the steps and means (tactically) to make those changes
- in a way that avoids system’s dysfunction
- with buy-in, consensus, and no resistance.
For those interested in learning more, I’m happy to chat, train, and share. Or feel free to use my thoughts to inspire your own model.
Listening for Systems: from birth we’re taught to carefully listen for content and try to understand the Other’s meaning (exemplified by Active Listening) which, because of our listening filters, often misses the underlying, unspoken Metamessage the speaker intends. By teaching the brain to disassociate and listen broadly rather than specifically, Systems Listening enables hearing the intended message at the root of the message being sent and supersedes all bias on either end. For those interested, read my article on how our listening restricts our worlds.
Facilitative Questions: conventional questions, used to gather data, are biased by the Speaker and interpreted in a biased way by the Responder. The intent of Facilitative Questions (FQ) is to lead listeners through a sequential discovery process through their own (often unconscious) status quo; not information focused and not biased, they are directive, and enable our CPs to discover for themselves the full range of elements they must address to achieve excellence. Here is a simple (out of sequence) example of the differences between conventional questions and FQs. Note how the FQ teaches the Other how to think:
- Conventional Question: Why do you wear your hair like that? This question, meant to extract data for the Speaker’s use, is biased by the Speaker and limits choices within the Responder. Bias/Bias
- Facilitative Question: How would you know if it were time to reconsider your hairstyle? While conventional questions ask/pull biased data, this question sequentially leads the Other through focused scans of unconscious beliefs in the status quo. Formulating them requires Listening for Systems.
Using specific words, in a specific order, to stimulate specific thought categories, FQs lead Others down their steps of congruent change, with no bias. Now we can be part of the process with them much earlier and use our desire to influence change to positive effect. We can actually help Others help themselves.
Steps of change: There is a habituated, idiosyncratic hierarchy of people, rules, values, systems, and history within each status quo. By helping our CPs navigate down their hierarchy they can discover and manage each point necessary to change without disruption or resistance. Until they know how to do this – and note, as outsiders we can NEVER understand this – they can take no action as their habitual functioning (their status quo) is at risk. Offering them our information is the final thing they’ll need when all of the change elements are recognized.
To me, being kind, ethical and true servants, being influencers who can make a difference, means helping Others be all they can be THEIR way, not OUR way. As true servant leaders and change agents we can facilitate real, lasting change and then, when Others know how to change congruently, our important solutions will be heard.
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen September 15th, 2025
Posted In: Communication, Listening
You Can’t Change a Behavior by Trying to Change a Behavior, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 I recently got a call from a noted venture capitalist of healthcare apps.
I recently got a call from a noted venture capitalist of healthcare apps.
DH: I heard you have a model that facilitates permanent behavior change. I wonder if it would work with any of the 15 healthcare apps I’ve invested in.
SD: I do have a model that does that. And it certainly could be used as a front end to conventional behavior change apps to enable users to develop permanent habits by developing neural circuits. What are you using now to help folks change behaviors permanently?
DH. Behavior Modification, but it doesn’t work. There’s no scientific evidence that it works and our analysis concurs. But there’s nothing else to use. Can you help?
It’s a known fact that Behavior Modification has a 3% success rate over time. Sure, people initially lose weight with a behavior-based plan to eat differently. Certainly people stop smoking or get to the gym for a few weeks. But because these new behaviors haven’t been accepted by, or made permanent in, the brain, they cannot succeed over time. And repeating the new in hopes that THIS time it will stick obviously doesn’t work.
Stay tuned for my new book: HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change, and decision making.
Permanent change is a very achievable goal. But we’re approaching the problem from the wrong angle. In this essay I will explain what a behavior is, what change is, how our brain governs them both, and introduce the steps needed to form habits. Believe it or not, it’s mechanical.
THE PROBLEM WITH BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION
Lately I’ve heard several Behavioral Scientists on the radio, all offering Behavior Modification techniques to habituate new behaviors by, well, habituating new behaviors. They ‘remove barriers’, suggest ‘momentum’, offer ‘promoting forces/restraining forces’, and propose ‘behavioral interventions’ such as keeping weights at your desk so you can ‘lift’ during Zoom calls. All meant to motivate behavior change – through behavior change. I suspect Einstein might have something to say about that.
The problem is the premise. Behavior Mod’s core assumptions are actually contrary to brain science. It assumes that by merely repeating (and repeating and repeating) new ways to accomplish something that’s been problematic, permanent change will result that can be maintained over time. But it doesn’t. And it can’t.
Certainly we’ve all tried. We’ve learned the hard way that we can’t lose weight permanently by trying to lose weight. Or stop smoking by trying to stop smoking. We promise ourselves we’ll be disciplined ‘this time’. But our discipline isn’t the problem. We have no circuits to translate our wishes into actions automatically. Our brain makes us fail.
DIFFERENT THINKING REQUIRED
The reason we fail is simple: we’re not making the necessary adjustments to the neural pathways that prompt behaviors to begin with.
I’ll start with an analogy. Let’s say you purchase a forward-moving robot, use it for a while, then decide you want it to move backward. You tell it why a ‘backwards’ functionality would enhance it, show it slides and presentations of other robots that move backwards, and attempt to push, cajole, and offer rewards. Nope. It won’t move backward. But if you program it differently, it will.
What about changing a chair into a table. You put red plastic into a machine that is programmed to spit out a red plastic chair. Once the chair is produced, you can’t make it a table. But you can create a table if you program the machine appropriately at the start.
Changing habits by trying to change habits is merely attempting to change the outcome – the output, the habit, the behavior, the robot, the chair – but failing to reprogram the brain with different instructions to create something new.
Sounds obvious. But that’s not what behaviorists do: the Behavior Mod approach suggests we get the robot to move backward by pushing it (and pushing it and pushing it) assuming the repetition will cause permanent change. As you know, it doesn’t work.
WHAT IS A BEHAVIOR?
To understand the full scope of the problem it’s helpful to understand what, exactly, a behavior is. They don’t just arise because we want them to. Behaviors are the output of our brain’s signaling system, the response to input instructions that travel as electrochemical signals down a fixed neural pathway and hook up with a set of circuits that translates the signals into something tangible.
Where do behaviors originate? Behaviors are Beliefs in action, physical representations of our core identity factors. Our politics represent our Beliefs. The way we dress, talk; the professions we choose; where we travel and who we marry. Everything we do represents who we are.
As the foundational factor in what we do and think, Beliefs must be factored in when considering change or forming a new habit. Current Behavior Mod approaches circumvent Beliefs and therein lie the problem.
There is actual science on how behaviors get generated and why we automatically repeat behaviors even when we don’t want to. Here’s a quote from noted Harvard neuroscientist Richard Masland in We Know It When We See It to set the stage:
Our brain has trillions of cell assemblies that fire together automatically. When anything incoming bears even some of the characteristics [of operational circuits], the brain automatically fires the same set of synapses [triggering the same behavior]. (pg 143).
Here’s a simplified version of how to convince the brain to make the changes that lead to new habits. It explains how behaviors occur and where change comes from. For a more complete explanation and tools to actually create new brain circuitry for change, watch for my new book HOW? coming out soon.
NEUROLOGICAL PATHWAY FROM INPUT TO OUTPUT
Generally, each behavior starts off as an input – an idea or command, thought or story – that enters our brain as a meaningless puff of air, an electrochemical vibration (a ‘message’). To keep us congruent, the input gets evaluated against our Mental Models and Beliefs before going further. Is this input a risk? Is it congruent with our values?
If the idea goes against who we are, it gets rejected or resisted. If the vibration is accepted, it gets turned into signals that then seek out (among our 100 trillion synapses) similar-enough circuits that translate them into action or output – a behavior. Specifically, our brains:
-
- receive input vibrations (from conversations, thoughts, reading, ideas, internal commands) and
- compare/test these against foundational Beliefs, norms, and history, after which they
- get turned into signals that get
- matched with the closest, ‘similar enough’ neural circuits
- that translate them into output/action/behavior.
As you can see, whichever neural circuits receive the signals are the translators that determine what we hear, see, know, and do. Simply stated it looks like this:
Input -> Risk check -> Signal creation and Dispatch -> Output
The time it takes a message to go from an input to an output takes 5 one-hundredths of a second. It’s pretty automatic. And obviously, once an output, it can’t be changed. Change begins when initiated from the input.
THE NEED FOR VALUES-BASED CONGRUENCY
The next important piece is why repetition won’t cause new (permanent) habits. When a wholly new input enters, it requires a new relevancy check. Sadly – and the reason new activity fails when Behavior Mod is attempted – if anything tries to change the status quo without being checked for relevance, our brain discards the new input because it may carry risk! The new isn’t sustainable without new circuitry.
When we try to create new habits by merely ‘doing’ new behaviors without sending new and different input instructions we cannot generate permanent change because there are no new circuits to administer it!
The good news is that the brain is always willing to create new circuits for new behaviors. It’s called Neurogenesis.
CREATING NEW PROGRAMMING, NEW SIGNALS, NEW BEHAVIORS
To change behaviors permanently, start with new input messages:
-
-
- create a new belief-based input/message that
- generates new signals which
- create or discover a different arrangement of circuits
- which translate them into new/different behaviors.
-
I’ll explain with a story. A friend said, “I’ve been telling myself I’m a Fat Cow recently. That means it’s time for me to go on another diet.” Obviously this input would lead her to the same circuits (and results) that it used for past diets that she failed at. But if she changed her input signal and told herself instead:
‘I am a healthy person who will research best nutrition choices for my body type and lifestyle and have the discipline to eat the best foods for the rest of my life.’
she would end up with a different set of circuits and different output/behaviors.
Our outputs, our behaviors, are merely responses to inputs that our brain has checked out as congruent with who we are. So one way to change a behavior is to change the incoming messaging to one that is Belief-based and takes into account all the elements (Mental Models, history, norms, experience) that might cause risk to the system. Once it’s approved, it will automatically generate new circuits and new, habituated, behaviors.
My new book How? Generating new neural pathways for learning, behavior change, and decision making, will teach you several models to formulate the neural circuits you need to help you change habits permanently.
I am passionately interested in enabling people to consciously design new signaling instructions for their brains to output any new habits they seek. My wish is to work with healthcare providers and apps for exercise, healthy eating, meditation and decision making to aid folks seeking to achieve greater health and success.
If you want to collaborate, or have questions, contact me to discuss ways we can engage those seeking permanent change. sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
_______________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen September 8th, 2025
Posted In: Change Management, Communication
Don’t Start Selling with Sales: facilitate back-end buying decisions first for a higher close rate, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 I’ve trained about 100,000 sales professionals globally. Before we begin, I ask them what training they receive as their sales job begins. They all say ‘Product knowledge.’ When I ask them if they know how their buyers are buying, they don’t even understand the question.
I’ve trained about 100,000 sales professionals globally. Before we begin, I ask them what training they receive as their sales job begins. They all say ‘Product knowledge.’ When I ask them if they know how their buyers are buying, they don’t even understand the question.
In my 40 years of teaching Buying Facilitation®, I’ve never met a sales person who knows their buyer’s buying decision process. And yet this is where, how, and why buyers eventually buy. By ignoring this, sellers reduce their close rate dramatically.
SALES STARTS TOO SOON
Sales and marketing direct their efforts on placing solutions, offering prospects great content, engaging graphics, and loyal customer reviews. And it works – 5% of the time.
What’s going on the other 95%? Well, those folks don’t need your solution details. Not at first anyway.
Before people self-identify as buyers, they have work to do: they try workarounds, manage their risk of change and get buy-in to do anything differently. Until then they have no interest in the information you offer.
In other words, your pitches, illustrations, and reviews will only be beneficial for people at the very end of their buying decision path. And that’s where you’re starting!
WHEN DO PEOPLE BUY?
People only buy when:
- There are no available workarounds;
- The risk of change is less than their risk of staying the same;
- The folks who will use the new solution agree to the change and have comfort learning how to use the new solution.
Buying is a change management problem before it’s a solution choice issue. Until people understand their risk of change, and until users buy-in to doing anything different, they will not buy regardless of what you’re selling or what they need.
Before people are ready to buy they must have these questions answered: How can they resolve their problem with the least disruption? Can a new solution fit with existing software and minimal training? How can the group generate buy-in so there’s no resistance? Who will supervise the implementation of the new solution over time?
In other words, until they have all their ducks in a row, people cannot self-identify as buyers and will ignore and rebuff your efforts.
I’m sure you know this. Hundreds of articles have been written on the 70% that goes on behind the scenes. So why aren’t you addressing this portion of the buying decision journey?
Even people who theoretically are great prospects can’t consider buying if the risk to their system, their culture, is too high, or if users won’t use it. They certainly cannot define their need until they do so.
I would think the low close rate would tell you there’s a problem with what you’re doing. My goodness, you wouldn’t even go to a hairdresser with a 5% success rate. You certainly wouldn’t get on a plane. Yet you continue to assume your solution will rule the day and base your entire approach on placing your solution. Facts tell you otherwise, and yet you ignore them.
Your solution is the last thing people need. Why not first help them with the backend work they must do anyway? Why not add some new tools and begin with a Change Management, or a Risk Management focus and help them first – and then they’ll already be working with you when they’re ready to buy? To do this, you’ll need to stop selling until they’re ready.
The question becomes: would you rather sell or have someone buy? You know the answer – but you’re acting as if the only process you need is selling….which ignores all but 5% of those those folks who will buy but aren’t ready. BTW these folks can easily be made ready! You can help them, decrease your sales cycle by one half, and close 40% from first call. But it requires a wholly different toolkit.
Sales is a Stage 2 model. First, Stage 1: facilitate buying (check out my Buying Facilitation® model). Then Stage 2: sell. To facilitate buying, you must:
- change your outreach to seek folks in the process of solving a problem your solution can fix. You’ll need to ask different questions to find folks on their problem-solving journey; listen differently to hear where they are in their journey, then help them through their change process. With a ‘need’ focus you’re merely posing biased questions and listening for an opening to pitch into. How many thousands of names have you thrown away – real prospects! – because they were still in their problem-solving phase and not yet ready?
o Rule: until people have gone through their entire risk- and change management process, they don’t even have a complete understanding of their need!
o Rule: don’t begin by seeking folks with need. Begin by seeking people on route to fixing a problem your solution can resolve and help them manage their change.
- put your solution knowledge on the back burner until you’ve helped people figure out their risk and change issues.
o Rule: you need a wholly different skill set to facilitate buying. Currently you’re only listening and posing questions so you can hear an opening to pitch into.
- seek people who WILL become prospects/buyers once they’ve got all their ducks in a row. Now you’re merely guessing who is a prospect (i.e. the 5% close rate should make that obvious).
o Rule: People cannot buy until they’ve figured out how to solve a problem with minimal disruption. Help them do this first.
- facilitate prospective buyers through their change/risk management before trying to sell. They’re doing it without you as you wait.
o Rule: People are now abusing your time to pull knowledge they can use to solve their own problem without you. Provide product information AFTER they’ve clearly defined their need.
There are 13 steps to any change process. Sales enters at the last 3 steps and seeks that small percentage of people who have completed their change process. This ignores the bulk of the buying decision journey – real prospects who you could quickly facilitate through their decisions to a close – to find those at the end.
Why not put on a Buying Facilitation® hat first, seek folks during their change and risk management processes; facilitate them through their change decisions, buy-in, and risk management; and then you’ll find real prospects on the first call and stop wasting time trying to convince people who just aren’t ready yet.
For those sellers interested in closing more and willing to learn new skills, I’d love to teach you Buying Facilitation®. Contact me: sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen September 1st, 2025
Posted In: Sales
Bridging the Gap between What’s Said and What’s Heard, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 I used to assume that what I hear someone say is an accurate interpretation of what they mean. My assumption was wrong; what I think I hear has a good chance of being inaccurate, regardless of how intently I listen. But it’s not my fault.
I used to assume that what I hear someone say is an accurate interpretation of what they mean. My assumption was wrong; what I think I hear has a good chance of being inaccurate, regardless of how intently I listen. But it’s not my fault.
During the years I spent reading, thinking, and researching for my book (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?) on closing the gap between what’s said and what’s heard, I was quite surprised to learn how little of what I think I hear is unbiased, or even accurate. Listening, it turns out, is a brain thing and has little to do with words or intent.
HOW BRAIN’S ‘LISTEN’
When we listen to others, we’re not directly hearing their words or intent but an interpretation of a set of meaningless, automatic neurological activities in our brain that have little-to-no relationship with what’s been said.
What we think we hear is wholly determined by our historic life experiences (education, family, values, Beliefs, mental models) that have been stored in our brain and filter all incoming words:what we hear someone say has been translated by what we’ve heard before, creating biases and assumptions that keep us from translating incoming messages accurately.
Generally speaking, our brain determines what we hear. And it’s not objective. Here’s what happens:
-
- Words are merely puffs of air that emerge from our lungs, formed by our mouth and tongue – meaningless sound vibrations – that enter a Listener’s brain and get made into signals that get sent to ‘similar-enough’, existing brain circuits for translation. In other words, there’s a high probability Listeners can’t accurately understand what’s been said because their brain has translated what’s been said by what they’ve heard before.
- A Listener’s ears
– capture some portion of incoming sound vibrations,
– conducts them through historic filters (Beliefs, mental models, etc.)
– translate the remaining vibrations into signals that get sent to
– match ‘similar-enough’ existing circuits, which
– discard what doesn’t match.
The remainder – with an undetermined relationship to what was intended is – what we think we ‘hear’.
-
- Listeners have no idea what has been discarded in the process of hearing/translating what’s been said. Statistically, we accurately hear no more than 35% of what’s been said.
- Both Speakers and Listeners have no idea how a Listener’s brain has interpreted or biased what been said or how close to accurate it’s been received. We all assume what we think we hear is accurate, although it rarely is.
- We speak in run-on sentences, not individual words, and a Listener’s brain must make sense of the variations in vibrations of each word.
- People speak for approximately 600 milliseconds; Listeners begin formulating their response in 200 milliseconds. Approximately two thirds of what’s been said is not even heard.
What we think we hear is some version of our history of hearing something similar. With people we’re in regular contact with and already have circuits to translate, it can be pretty accurate. With others not so much.
DIAGRAM OF HOW BRAINS ‘LISTEN’
Herein lie the gap between what’s said and what’s heard: we all make inaccurate assumptions of what we think we hear, causing us to respond and choose actions from a restricted or flawed knowledge base. Of course, it’s not done purposefully, but it sure plays havoc with communication and relationships.
I once lost a business partner because he misinterpreted something he thought I said, even though his wife told him he had misheard. His comment: “I heard it with my own ears! Are you both telling me I’m crazy??” and stormed out, never to speak to me again.
Unfortunately, and different from perceived wisdom, brains don’t allow us to ‘actively listen’ to accurately understand what’s been said. Sure, Active Listening allows us to ‘hear’ the words spoken but doesn’t capture the intent, the underlying meaning. And given our neurological hearing processes are automatic, mechanical, and thoughtless, we’re stuck with what we think we hear. Here’s a simplified diagram of the process of listening:
Incoming sound vibrations as electrochemical signals get distorted and deleted through the brain’s filtering and transmission processes, eventually getting translated by ‘similar-enough’ existing neural circuits causing us to hear some rendition of what we’ve heard historically. There’s little chance any of us can understand a Speaker’s intended meaning accurately.
GUIDELINES TO MAXIMIZE UNDERSTANDING IN DIALOGUE
Given how vital listening is to our lives, for those times we want to make sure we understand and get on the same page with a Communication Partner (CP) to reach consensus, here are some guidelines:
Get agreement for a dialogue: Often, Communication Partners have different life experiences and, potentially different goals – many of which might be unconscious. Begin by agreeing to find common ground.
“I’d like to have a dialogue that might lead to us to a path that meets both of our goals. If you agree, do you have thoughts on where you’d like to begin?”
“I wonder if we can find common goals so we might find agreement to work from. I’m happy to share my goals with you; I’d like to hear yours as well.”
Set the frame for common values: At a global level, we all have similar foundational values, hopes and fears – for family, food, shelter, health. Start by ‘chunking up’ to find areas of agreement.
“I’d like to find a way to communicate that might help us find a common values so we can begin determining if we share areas of agreement. Any thoughts on how you’d like to proceed?”
“It seems we’re in opposite mind-sets. How do you recommend we go about finding if there’s any agreement we can start from?”
Get agreement on the topics in the conversation: One step at a time; make sure CPs agree to each item and skip the ones (for now) where there’s no agreement. (Put them in a Parking Lot for your next conversation.) Work with ‘what is’ instead of ‘what should be.’
Enter without bias: Unintentionally our historic, unconscious beliefs restrict our search for commonality. Replace emotions and blame with a new bias for this conversation: the ‘bias’ of collaboration.
“I’m willing to find common ground and would like to put aside my normal reactions for this hour but it will be a challenge since my feelings are so strong. Do you also have strong feelings that also might bias our communication? I wonder if we could share our most cherished beliefs and then discuss how we can move forward without bias.”
Get into Observer: To help overcome unconscious biases and filters, here are a few mind hacks that will supersede automatic brain processing: in your mind’s eye, see yourself on the ceiling looking down on yourself and your CP. I call this the Observer (witness, coach) position. It will provide a different viewpoint for your brain, replacing the emotional, automatic response with a broader, far less biased, view of your interaction. Another way is to walk around during the conversation, or sit way, way back in a chair. Sitting forward keeps you in your biases. (Chapter 6 in What? teaches how to stay in Observer and reduce bias.). From your Observer place, notice elements of the communication of both you and your CP:
-
-
- Notice body language/words: Similar to how your brain filters incoming words, your CP is speaking/listening from their filters and assumptions, which will be exhibited in their body language and eye contact. From Observer notice how their physical stance matches their words, the level of passion, feelings, and emotion. Now look down and notice how you look and sound in relation to your CP. Just notice. Read Carol Goman’s excellent book on the subject.
- Notice triggers: Emphasized words hold beliefs and biases. You may also hear absolutes: Always, Never; lots of You’s may be the vocabulary of blame. Silence, folded arms, a stick-straight torso may show distrust. Just notice where/when it happens for you both. If your CPs words trigger you into your own subjective viewpoints, you’ve gotten out of Observer and must get back onto the ceiling where you have choice. But just in case:
-
“I’m going to try very hard to speak/listen without my historic biases. If you find me getting heated, or feel blame, I apologize as that’s not my intent. If this should happen, please tell me you’re not feeling heard and I’ll do my best to work from a place of compassion and empathy.”
Summarize regularly: Because the odds are bad that you’ll accurately hear what your CP means to convey, summarize what you think you heard after every exchange:
“Sounds to me like you said, “XX”. Is that correct? What would you like me to understand that I didn’t understand or that I misheard?”
“I’ statements: Stay away from ‘You’ if possible. Try to work from the understanding that you’re standing in different shoes and there is no way either of you can see the other’s landscape.
“When I hear you say X it sounds to me like you are telling me that YY. Is that true?”
“When I hear you mention Y, I feel like Z and it makes me want to get up from the table as I feel you really aren’t willing to hear me. How can we handle this so we can move forward together?”
Get buy-in each step of the way: keep checking in, even if it seems obvious that you’re on the same page. It’s really easy to mistranslate what’s been said when the listening filters are different.
“Seems to me like we’re on the same page here. I think we’re both saying X. Is that true? What am I missing?”
“What should I add to my thinking that I’m avoiding or not understanding the same way you are? Is there a way you want me to experience what it looks like from your shoes that I don’t currently know how to experience? Can you help me understand?”
Check your gut: Notice when/if your stomach gets tight, or your throat hurts. These are sure signs that your beliefs are being stepped on and you’re out of Observer. Get back up to the ceiling and then tell your CP:
“I’m experiencing some annoyance/anger/fear/blame. That means something we’re discussing is going against one of my beliefs or values. Can we stop a moment and check in with each other so we don’t go off the rails?”
Get agreement on action items: Simple steps for forward actions will become obvious; make sure you both work on action items together.
Get a time on the calendar for the next meeting: Make sure you discuss who else needs to be brought into the conversation, end up with goals you can all agree on and walk away with an accurate understanding of what’s been said and what’s expected.
COMPASSION, EMPATHY, AND RESPECT
Until or unless we all hold the belief that none of us matter if some of us don’t; until or unless we’re all willing to take the responsibility for each (inadvertent)act of harm; until or unless we’re each willing to put aside our very real grievances to seek a higher good, we’ll never heal.
It’s not easy. But by learning how to hear each other with compassion and empathy, by closing the gap between what’s said and what’s heard, our conversations can begin. We must be willing to start sharing our Truth and our hearts and find a way to join with another’s Truth and heart. By hearing each other accurately, it’s the best start we can make.
______________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen August 25th, 2025
Posted In: Listening
Conscious Failing, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 As a preamble to a discussion about failing consciously, I’d like to retell a story. Many years ago Xerox was beta testing a then new-type digital printer. The testers sent back complaints: it was hard to figure out how to work the damn thing, and the user guide was confusing. Obviously, User Error, the designers concluded. Yup. More stupid users. So an internal focus group was set up by senior management to test what exactly was happening.
As a preamble to a discussion about failing consciously, I’d like to retell a story. Many years ago Xerox was beta testing a then new-type digital printer. The testers sent back complaints: it was hard to figure out how to work the damn thing, and the user guide was confusing. Obviously, User Error, the designers concluded. Yup. More stupid users. So an internal focus group was set up by senior management to test what exactly was happening.
Three middle managers were brought in and put into a room with the new printer and user guide. Mayhem ensued. The designers watched from behind a one-way mirror while the managers got confused by the directions, spent hours arguing amongst themselves, pressed the wrong buttons, and finally gave up – never getting it to work.
User Error, they again said. Obviously, went the thinking, the managers weren’t smart or savvy enough to understand simple directions. Except they didn’t know a trick had been played on them: the testers were actually PhD computer scientists. Oops. It wasn’t User Error at all. The designers had failed to develop an intelligible user guide. So while the printer itself might have been a marvel of machinery for its day, it couldn’t be used. It was a failure. Or was it?
WHAT IS FAILURE
I contend that until every ‘failed’ step was taken, and every ‘failed’ assumption made, there was no way to know exactly what problems needed to be fixed or if indeed their printer was a success. The failure was part of the march to success.
We call it failure when we don’t achieve a goal whether it’s starting up a company, reaching a job goal, learning something new, or starting a new diet.
I think that as humans we strive to succeed, to be seen as competent, to be ‘better than’, even if we’re only in competition with ourselves. It’s natural to want our products, our teams, our families, our competitive activities, to reap success. To be The Best. And we plot and envision how to make it happen.
But the road to success isn’t straight; sometimes we face disappointment, shame, and self-judgment. We get annoyed with ourselves when results don’t seem to comply with our mental images, and tell ourselves maybe we didn’t follow the original plan, or didn’t plan well enough, or maybe we’re self-sabotaging. We blame teammates or vendors, spouses or neighbors.
I’m here to tell you that failure is a necessary part of success. It’s built in to learning and succeeding, actually a natural part of the process of change and accomplishment. Before we win we gotta fail. Tiger Woods didn’t wake up the best in the world. Neither did Pavarotti or Steve Jobs.
For anyone to get to the top, to achieve success in any industry, any endeavor, any sport, it’s necessary to fail over and over. How surprising that no one teaches us how to fail consciously. I suggest we develop conscious failing strategies that become built in to our success procedures.
WHAT IS OUR STATUS QUO? AND WHY IS IT SO STUBBORN?
Getting to success is a sequential process that includes trial and error – i.e. winning and losing are both part of the same process, and each adding a piece of the puzzle. Of course there’s no way to know what we don’t know before we start – no way to even be curious, or ask the right questions because we don’t know what we don’t know. And unfortunately, part of the process is internal, unconscious, and systemic.
Change – and all success and failure is really a form of changing our status quo – has a large unconscious component, and when you only try to add new behaviors you miss the automatic, habituated, and unconscious elements that will rear their ugly heads as you move toward hitting your goals: you can’t change a behavior by trying to change a behavior. It just doesn’t work that way.
Let me explain a few things about how your brain works in the area of change. To begin, all change is systemic. Anything new you want to do, anything new that requires, ultimately, new behaviors, or added beliefs or life changes, requires buy-in from what already exists in your make up – your status quo.
Indeed, as the repository of your history, values, and norms, your status quo won’t change a thing without congruency. Indeed it will reject anything new, regardless of how necessary it is, unless the new has been properly vetted by the originating system.
Setting a goal that’s behavior-based without agreement from the system, without incorporating steps for buy in, assures resistance. Sure, we lay out the trajectory, attempt to make one good decision at a time, and use every feeling, hope, data point, guess, to take next steps. But when we don’t take into account the way our brains unconsciously process, it may not turn out like we envision. Lucky there’s a way to manage our activities to take into account what a brain needs for congruent change and a successful outcome.
THE STEPS TO FAILING CONSCIOUSLY
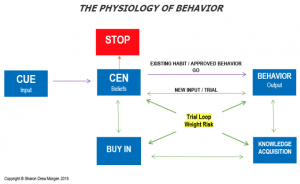
In my work on how brains facilitate change and make decisions to shift what’s already there (my The How of Change program teaches how to generate new neural routes) I offer ways to create new synapses and neural pathways that lead to new behaviors. Take a look at the Change Model chart I developed, with a careful look at The Trial Loop – the steps we each take to learn, to add/trial something new:
The Trial Loop is where the brain learning occurs. It’s here we iterate through several touch points: new data acquisition, buy-in, trial behaviors, and the stop/go/stop action (double-arrowed line between Beliefs (CEN) and red Stop) as each new element is tried and considered before new behaviors are formed.
It’s important to understand that no change will occur until these elements are addressed; merely hearing something new – a directive, an interesting piece of information, an internal decision to change a behavior – doesn’t insure something different will happen. Unless our system buys in, until there’s a specific circuit created for the new, no change will occur. You can’t change a behavior by trying to change a behavior.
So as we try out new stuff, our personal mental models of rules, beliefs, norms, history, etc., go through iterations of trial, acceptance, rejection, confusion, trial, acceptance, rejection, etc. until the new is congruent with the norms of the system, something we cannot know before we go through this process. So let’s call our disappointments part of the iteration process that precedes success. Here is a closer look at my chart:
- An initial goal/idea/thought enters (through the CUE),
- then gets sorted through an acceptance/rejection process for beliefs and systems congruence (the CEN), which
- darts around the brain seeking a match for an existing neural pathway for earlier incidence of achieving this goal.
- If no existing pathway is found, a new synapse/neural pathway must be formed.
- The brain goes through an iterative process to form a new path to a new action with agreement (buy in) needed at each step (notice the iterative arrows in the chart).
- Iterative process includes: gathering data, trialing new activity, getting internal buy in, testing for Systems Congruence (All systems must be in a congruent state. Individually and personally, we’re all a system.)
- Process of Stop/New choice-data acquisition-action/Stop etc. as each new thing is tried.
- Final success when there’s congruency and new is adopted without resistance as a final Behavior. (And note: the Behavior is the FINAL activity. You cannot change a behavior by trying to change a behavior.)
Now you know the steps to conscious change. Should you want to learn more here’s a one-hour sample of me laying out the foundation of the How of Change course and explaining how change occurs in the brain.
THE STEPS TO CONSCIOUS FAILING
Now let’s plot out the steps to conscious failure to avoid large-scale malfunction.
The Beginning: to start the process toward succeeding at a goal, you need:
- Include all (all) stakeholders (including Joe in accounting) and all who will touch the final solution;
- Agree upon the wording for the final goal, including specifics of new behavioral elements, rules, politics, outcomes – i.e. what, exactly, will be different;
- Write up a ‘guess list’ of problems that might occur (failures) to the status quo as a result: what they might look like, as well as possible workarounds;
- An agreement clause from all stakeholders to act when something is going off course. Note: listening without bias is urgently needed here;
- Consider possible ways your starting goals may shift the status quo and make sure it’s tenable;
- Know how the new outcome will be maintained over time (including the people, rules, norms, changes, that will be involved) and what else has to buy in to maintenance;
- State potential, detailed steps toward achievement that are agreeable to all stakeholders;
- Agreement to reconsider all previous steps if the problems that show up cause new considerations.
The Middle: to make changes, add new knowledge to trial, get continuous buy in, you need:
- Re write the original goals, with delineated outcomes for each;
- Notice how the new is disrupting the status quo. Is it necessary to amend the new plans to ensure Systems Congruence? Is the cost of the new lower than the cost of the original? There must be a cost-effective decision made;
- Find ways to acquire the right knowledge to learn from;
- Check on the ways you’re failing. Were they expected? Do they conform to your goals? Do you need to shift anything?
- Agreement to develop new choices where current ones aren’t working as per plan.
The End: making sure the outcome is congruent with the original goal:
- Go through the Beginning steps and check they’ve been accomplished;
- Compare end result with original goal;
- Make sure there is congruent integration with the thinking, beliefs, values of the original;
- Make sure the status quo is functioning without disruption and the system ends up congruent with its mental models and belief systems.
Here are more specifics to help you integrate the necessary failure, and avoid guesswork and reactions to what might seem inconsistent with your goals:
- Lay out specifics for each step you’re considering to your goal. Include timelines, parameters, and consequences of results, specific elements of what success for that step should look like, and what possible failure might look like. Of course, you can’t truly know the answers until they occur, but make your best guess. It’s important to notice something new happening when it’s happening.
- If something unplanned or feared occurs (i.e. failure), annotate the details. What exactly is happening? What elements worked and what didn’t, and how did they work or not work – what/who was involved, how did the result differ from the expectations? What does the failure tell you – what IS succeeding instead of what you wish for? How does the remedy for the problem influence the next step? How long should you allot for each occurrence before determining whether it’s failure, or just part of the success trajectory you weren’t aware of?
- Are all stakeholders involved and shared their input? Do you need to bring in more stakeholders?
- Notice the consequences of the outcomes for each: employees, clients, hiring, firing, quitting, vendors, competition, state of the industry and your place in it. What comes into play with these factors when considering if you want to continue down one trajectory rather than designing a new one? What will it look like to decide to change course? How will your decisions effect your vision of an outcome? How are the stakeholders affected by each choice?
- How much failure are you willing to risk before you determine that either your outcome is untenable, or you need to make structural changes? What part does ego and denial play? Does everyone agree what constitutes failure? Success?
- What will you notice when your trajectory to success is negatively effecting your baseline givens? What are you willing to change, or accept, to reach your goal?
- What will it look like, specifically, when you’ve concluded your efforts? Will parts of the failure be factored in as success? Do all stakeholders buy in to the end result? If not, what remains unresolved? And how will you bring this forward?
Of course there’s no way to know before you start what any specific stage will look like. But using the steps, the thinking, above, you’ll be able to get a handle on it. And by including the failure, you’ll have a far better chance of succeeding.
For some reason, as leaders or individuals, companies or small businesses, we shame ourselves when we don’t achieve what we set out to achieve during our change processes. I contend we must think of each step as an integral part of the process of getting where we want to be. As they say in NLP, there’s no failure, only feedback.
________________________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen August 18th, 2025
Posted In: Change Management, Communication
Sales as a Spiritual Practice


With untold millions of sales professionals in the world, sellers play a role in any economy. As the intermediary between clients and providers, sales can be a spiritual practice, with sellers becoming true facilitators and Servant Leaders (and close more sales).
The current sales model, directed at placing solutions and seeking folks with ‘need’, closes 5% – only those ready to buy at point of contact. Sadly, this ignores the possibility of facilitating and serving the 80% of folks on route to becoming buyers and not yet ready.
Until people have tried, and failed, to fix their problem themselves, understood and managed the risk and disruption that a new solution might cause their environment, they aren’t buyers. It’s only when they:
- know how to manage the risk of bringing in something new,
- can’t fix the problem themselves,
- get buy-in from whomever will touch the final solution,
- understand that the cost of bringing in something new is lower than the cost of maintaining the status quo,
will they self-identify as buyers and be ready to buy.
Indeed: buying is a risk/change management problem before it’s a solution choice issue, regardless of the need or the efficacy of the solution. All potential buyers must go through this process anyway – and the sales model doesn’t help.
WHY PEOPLE BUY
People don’t start off wanting to buy anything; they merely seek to resolve a problem at the least ‘cost’ (risk) to their system. Even if folks eventually need a seller’s solution, until they understand how to manage the change a new solution would generate, they won’t heed our outreach, regardless of their need or the efficacy of the solution. As a result, sellers with worthwhile solutions end up wasting a helluva lot of time being ignored and rejected.
Selling doesn’t cause buying. Sales focuses on only the final steps of a buying decision and overlooks the high percentage of would-be prospects who WILL become buyers once they’ve addressed their possible risk issues. After all, until they’ve recognized that the risk of the new is less than the risk of staying the same they won’t do anything different.
It’s not the solution being sold that’s the problem, it’s the process of pushing solutions before first helping those who will become buyers facilitate their necessary change process. Instead of a transactional process, sales can be an expansive, collaborative experience between seller and buyer.
As a result, sellers end up seeking and closing only those ready to buy at the point of contact – unwittingly ignoring others who aren’t ready yet, may need our solutions, and just need to get their ducks in a row before they’re prepared to make a decision.
Imagine having a product-needs discussion about moving an iceberg and discussing only the tip. That’s sales; it doesn’t facilitate the entire range of hidden, unique change issues buyers must consider – having nothing to do with solutions – before they could buy anything. Failure is built in.
But when sellers redirect their focus from seeking folks with ‘need’ to those considering change and lead them through their change management process before selling, they can facilitate them through the issues they must resolve (politics, relationships, resource, budget, time), help them assemble the right stakeholders from the start, and help them figure out how to address the disruption of bringing in a new solution. Then sellers become true servant leaders, inspire trust, and close more sales.
WHY SALES FAILS
Seller’s restricted focus on placing solutions, and listening for needs (which cannot be fully known until the change management process is complete) all but insures a one-sided communication based on the needs of the seller:
- Prospecting/cold calling – sellers pose biased questions as an excuse to offer solution details omitting those who will buy – real buyers! – once they’re ready. Wholly seller-centric.
- Content marketing – driven by the seller to push the ‘right’ data but really only a push into the unknown and a hope for action. Wholly seller-centric.
- Deals, cold-call pushes, negotiation, objection-handling, closing techniques, getting to ‘the’ decision maker, price-reductions – all assuming buyers would buy if they understood their need/the solution/their problem, all overlooking the real connection and service capability of addressing the person’s most pressing change issues. Wholly seller-centric.
To become a spiritual practice, sellers must use their expertise to become true facilitators that become necessary components in all buying decisions. Indeed, the job of ‘sales’ as merely a solution-placement vehicle is short-sighted.
- Buyers can find products online. They don’t need sellers to understand the features and benefits.
- Choosing a solution isn’t the problem. It’s the time it takes to manage the risk. – it’s the buyer’s behind-the-scenes timing, buy-in from those who will touch the solution, and change management process that gums up the works.
- The lion’s share of the buying decision (9 out of a 13 step decision path) involves buyers traversing internal change with no thoughts of buying. They don’t even self-identify as buyers until they understand their risk of change.
Since the 1980s, I’ve been an author, seller, trainer, consultant, and sales coach of the Buying Facilitation® model. And though I’ve trained 100,000 sales professionals, and wrote the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity, sales continues to be solution-placement driven. By ignoring a large population of potential buyers who merely aren’t ready, sales unwittingly ignores the real problem: it’s in the buying, not the selling.
SERVE PROSPECTS, CLOSE MORE SALES
It’s possible to truly serve clients AND close more sales.
Aspiring to a win-win
Win-win means both sides get what they need. Sellers believe that placing product that resolves a problem offers an automatic win-win. But that’s not wholly accurate. Buying isn’t as simple as choosing a solution. The very last thing people want is to buy anything, regardless of their apparent need.
As outsiders sellers can’t know the tangles of people and policies that hold a problem/need in place. The time it takes them to design a congruent solution that includes buy-in and change management is the length of their sales cycle. Buyers need to do this anyway; it’s the length of the sales cycle.
If sellers begin by finding those on route to buying and help them efficiently traverse their internal struggles, sellers can help them get to the ‘need/purchase’ decision more quickly and be part of the solution – win-win. No more chasing those who will never close; no more turning off those who will eventually seek our solution; no more gathering incomplete data from one person with partial answers.
Sellers can find and enable those who can/should buy to buy in half the time and sell more product – and very quickly know the difference between them and those who can never buy.
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts
There are several pieces to the puzzle here.
- The buyer and the environment the prospect lives in, including people, policies, job titles, egos, relationships, politics, layers of management, rules, etc. that no one on the outside will ever understand. It’s never as simple as just changing out the problem for a new product; they will buy only when they’re certain they can’t fix their own problem.
- Resolving the problem needs full internal buy-in before being willing to change (i.e. buy) regardless of the efficacy of the fix. A purchase is not necessarily their best solution even if it looks like a fit to a seller.
- The ability of the buyer to manage the disruption that a new purchase would incur on the system, people, and policies. A fix, or purchase, might be worse than the problem.
- The seller and the seller’s product may/may not fit in the buyer’s environment due to idiosyncratic, political, or rules-based issues, regardless of the need.
- The purchase and implementation and follow up that includes buy-in from all who will experience a potentially disruptive change if a new solution enters and shifts their job routines.
There is no right answer
Sellers often believe that buyers are idiots for not making speedy decisions, or for not buying an ‘obvious’ solution. But sales offers no skills to enter earlier with a different skill set to facilitate change or manage risk.
Once buyers figure out their congruent route to change, they won’t have objections, will close themselves, and there’s no competition: sellers facilitate change management first and then sell once everything is in place. No call backs and follow up and ignored calls. And trust is immediate: a seller becomes a necessary partner to the buying decision process.
No one has anyone else’s answer
By adding Buying Facilitation®, collaborative decisions get made that will serve everyone.
Let’s change the focus: instead relegating sales to merely a product/solution placement endeavor, let’s add the job of facilitation to first find people en route to becoming buyers, lead them through to their internal change process first, and then using the sales model when they’ve become buyers.
We can help people self-identify as buyers quickly, with fewer tire-kickers, better differentiation, no competition, and sales close in half the time.
BUYING FACILITATION®
As a seller and an entrepreneur (I founded a tech company in London, Hamburg, and Stuttgart in 1983), I realized that sales ignored the buying decision problem and developed Buying Facilitation® to add to sales as a Pre-Sales tool.
Buyers get to their answers eventually; the time this takes is the length of the sales cycle, and selling doesn’t cause buying. Once I developed this model for my sellers to use, we made their process far more efficient with an 8x increase in sales – a number consistently reproduced against control groups with my global training clients over the following decades.
Buying Facilitation® adds a new capability and level of expertise and becomes a part of the decision process from the first call. Make money and make nice.
Sellers no longer need to lose prospects because they’re not ready, or cognizant of their need. They can become intermediaries between their clients and their companies; use their positions to efficiently help buyers manage internal change congruently, without manipulation; use their time to serve those who WILL buy – and know this on the first contact – and stop wasting time on those who will never buy. It’s time for sellers to use their knowledge and care to serve buyers and their companies in a win-win. Let’s make sales a spiritual practice.
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen August 11th, 2025
Posted In: Communication, Listening, Sales
Unconscious Listening Biases: how influencers unwittingly restrict possibilities, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 Do you enter conversations to listen for what will confirm your assumptions? Do you assume the responses to your questions provide an accurate representation of the full fact pattern from which to base follow-on questions? Do you assume your history of similar topics topics gives you a more elevated understanding of what your Communication Partners (CPs) mean?
Do you enter conversations to listen for what will confirm your assumptions? Do you assume the responses to your questions provide an accurate representation of the full fact pattern from which to base follow-on questions? Do you assume your history of similar topics topics gives you a more elevated understanding of what your Communication Partners (CPs) mean?
If any of the above are true, you’re biasing your conversation. By entering conversations with assumptions and personal goals, and listening through your historic, unconscious filters, you unwittingly direct conversations to what you expect to hear and may miss a more optimal outcome. But it’s not your fault.
OUR BRAINS BIAS WHAT WE HEAR
The most surprising takeaway from my year of research for my book (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?) on closing the gap between what’s said and what’s heard was learning how little of what we think we hear is unbiased, or even accurate. Indeed, it’s pretty rare for us to hear precisely what another intends us to hear: our brains don’t allow us to.
Our brains listen through our existing neural circuitry, reducing our ability to accurately translate what’s been said to what we already know, leaving us unaware there might be a misunderstanding regardless of how carefully we listen.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how brains listen. Sound actually enters our ears as meaningless sound vibrations which become electrochemical signals that are dispatched to a similar-enough synapse. Unfortunately, whatever doesn’t match exactly gets deleted. We’re left assuming that what we think we’ve ‘heard’ is accurate even though there’s a good chance it’s not.
So your CP might say ABC and your brain tells you they said ABL without even mentioning it omitted D, E, F, etc. I once lost a business partner because he ‘heard’ me say X when three of us confirmed I said Y. “I was right here! Why are you all lying to me! I KNOW she said that!” And he walked out in a self-generated rage. This makes it tough for any communication where mutual understanding is so important.
Indeed, as outsiders – as sellers, leaders, or influencers of any kind – with different beliefs/values, backgrounds, etc., and entering conversations with our own goals and unconscious biases, we end up unintentionally misunderstanding, mistranslating, or mishearing, but believe what we think we’ve heard is true. In other words, our natural inability to hear accurately causes us miscommunication and flawed understanding. Not to mention lost business and lost relationships.
Net net, we unwittingly base our conversation, questions, and intuitive responses on an assumption of what we think has been said, and succeed only with those whose biases match our own. [Note: for those who want to manage this problem, I’ve developed a work-around in Chapter 6 of What?)
ENTERING CONVERSATIONS WITHOUT BIAS
I want to go back to the problems incurred by entering conversations with personal biases:
- by biasing the framework of the conversation to the goals we wish to achieve, we overlook alternative, congruent outcomes. Sellers, coaches, leaders, and managers often enter conversations with personal expectations and goals rather than collaboratively setting a viable frame and together discovering possibility.
- by listening only for what we’re (consciously or unconsciously) focused on hearing, we overlook a broader range of possible outcomes. Sellers, negotiators, leaders, help desk professionals, and coaches often miss real opportunities to promote agreement and discovery.
Here are some ideas to help you create conversations that avoid restriction:
- As an influencer, shift your goal from information gathering (for you) to facilitating the route to change (for them).
- Enter each conversation with a willingness to serve the greater good within the bounds of what you have to offer, rather than meet a specific outcome. Any expectations or goals limit outcomes.
- Enter with a blank brain, as a neutral navigator, servant leader, change facilitator.
- Trust that your CP has her own answers. Your job is to help her find them, as they are often unconscious. This is particularly hard for influencers who believe they have ‘the answers’. (And yes, all influencers, sellers, leaders, negotiators, and coaches are guilty of this.) I’ve written an article to specifically address this.
- Your biased questions will only extract biased answers. Use questions that make their journey to discovery more efficient, like “What has stopped you from making the change before now?”. [Note: I’ve developed Facilitative Questions that lead folks through their unconscious thinking patterns.]
- Enable Others to discover their own route to Excellence rather than attempt to influence a specific behavior you might deem important.
- Get rid of your ego, your need to be right or smart or have the answers. Until your CP finds a way to recognize their own unconscious issues, and design congruent change that matches their idiosyncratic ‘givens’, you aren’t helpful regardless of how much you know.
By listening with an ear that hears avenues to serve, to understand what’s been said without unconscious bias, you can truly serve your Communication Partner.
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen August 4th, 2025
Posted In: Listening
‘Send me an email’ indicates rejection, by Sharon-Drew Morgen
 I just read a discussion stream on LinkedIn debating why you’re told ‘Send me an email.’ when prospecting. It’s simple: you’re being rejected. People want to remove themselves from your push. It’s a problem created by the sales model itself.
I just read a discussion stream on LinkedIn debating why you’re told ‘Send me an email.’ when prospecting. It’s simple: you’re being rejected. People want to remove themselves from your push. It’s a problem created by the sales model itself.
I want to begin with a question that has plagued me since I ran a How Buyers Buy training program for KLM in 1987 when teaching them how to integrate the Buy Side into sales: Would you rather sell, or have someone buy?
You’ll say you’d prefer that someone buy. But your continued focus on the Sell Side largely ignores the Buy Side, causing you to struggle unnecessarily getting call-backs, closing, making appointments. Or equally ineffective, you assume your solution, your knowledge, your personality will facilitate buying. It doesn’t.
Surely you’ve realized that the Sell Side is quite different from the Buy Side. Two different activities and mind sets, both involved in a purchase, yet only one of them is addressed in your sales process.
SELLING VS BUYING
Buying is a How, a strategic change problem. Selling is a What and Why, a tactical solution placement problem. Buying involves cultural change and risk to the jobs, resources, and norms of the buyer. Selling involves finding people to give you money for your solution. Two different things requiring wholly different skills, goals, and intentions.
Selling doesn’t cause buying; buying is a change/risk management issue before it’s a solution choice. The very act of selling and your approach to each contact; the very questions you pose and assumptions you make; the content you share causes resistance with all but those 5% ready to buy.
Before people self-identify as buyers they have work to do…work not related to need or purchase, and certainly not involved with what you’re selling: until people manage and get buy-in for their risk of internal change and have tested workarounds – How, rather than What and Why – they cannot risk bringing in something new. In fact, a new solution is the last thing they need. Literally. And the sales model does not address this majority element of a buying decision.
SALES PLACES SOLUTIONS
The goal of sales is to place solutions: Find people who need what you’re selling, ask questions to confirm, then pitch. It assumes:
- you’re asking the right questions at the right time in their change/decision cycle and you can listen without bias;
- the prospect knows specifically what an external solution must include to be incorporated into their system congruently;
- the prospect has completed their 13 steps of change, tested workarounds, and gotten necessary buy-in;
- the person you’re speaking with speaks for the buying decision team, and knows all their criteria for change and risk;
- the risk of bringing in your solution has been managed.
Folks who haven’t yet completed their necessary change/risk management process ignore sellers: they’re still trying to solve their problem internally and haven’t considered going ‘outside’ for a fix. These are the folks who agree to meetings just to take your information. Or the folks who won’t take a call, even though they might later (once they’ve got all their ducks in a row) discover they need you.
By starting with a different goal (i.e. NOT need, but Change Facilitation) and skill set (Listening for Systems, Facilitative Questions™, 13 Steps of Change, etc.), these folks can be easily found and quickly facilitated through their steps of change with their stakeholders included. Once this is done, they buy quickly. With no rejection.
All people must figure this stuff out before they self-identify as buyers, with you or without you. Because of the rigid focus of the Sell Side, they do this without you, leaving you selling to the low hanging fruit – a 5% close rate.
WHY SALES FAILS
The sales model turns a seller into a hammer looking for a nail. It ignores three quarters of the real buyer’s decision journey.
Back in the day when Dale Carnegie told you to sell to need the buying process was much simpler. By maintaining that model, sales has become a stigmatized process that pushes content per the needs of the seller – the reason sales closes such a small percentage, and the reason sellers are told to ‘send me an email’.
Buyers have one criteria:to fix their problem with the least disruption to their system or they will maintain their status quo! The risk of the change must be equal to, or less than, the risk of staying the same. The time it takes them to figure all this out is the length of the sales cycle.
A buying decision is a risk management problem before it’s a solution choice. And the sales model – the Sell Side – doesn’t include facilitating change and risk – the Buy Side – which must be completed before people self-identify as buyers.
So long as you use the sales model as your only tool to facilitate a buying decision, you will have difficulty closing. That’s just not how buyers buy.
FACILITATE BUYING FIRST; SALES SECOND
What if you begin selling by
- using a Change Facilitation model to first search for people solving a problem your solution can resolve,
- then facilitate them through their risk and change,
- help them get buy-in from all who will touch the new solution,
- sell when they’re ready to buy.
It would require new skills but you’d find real prospects on the first call and close in half the time. Are you willing to learn a new skill to facilitate buying?
I’ve invented Buying Facilitation® (Stage 1, Buy Side) process to first find folks during their problem-solving phase and help them through their change/risk management and buy-in. Then sales (Stage 2, Sell Side) places the solution.
You need both. Call me if you want to learn Buying Facilitation® and increase your sales to 40% close. Do you want to sell? Or have someone buy?
__________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including her new book HOW? Generating new neural circuits for learning, behavior change and decision making, the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen July 28th, 2025
Posted In: News








