‘No Decision’ isn’t Indecision: people won’t buy until they’re buyers
 I’ve been reading articles claiming a major impediment to closing sales is buyer’s ‘indecision’. But is non-buying called ‘indecision’ because people aren’t responding according to a seller’s expectations? Why is an entire field built upon persuading Others to act as per the needs of a stranger who has no understanding of the Other’s internal (and highly idiosyncratic) benchmarks?
I’ve been reading articles claiming a major impediment to closing sales is buyer’s ‘indecision’. But is non-buying called ‘indecision’ because people aren’t responding according to a seller’s expectations? Why is an entire field built upon persuading Others to act as per the needs of a stranger who has no understanding of the Other’s internal (and highly idiosyncratic) benchmarks?
Why do sellers think by ‘painting a compelling reason’ for prospects who have ‘cold feet’, or by providing a ‘burning platform’ to entice buying, they must get people to um, understand that ‘the pain of same is worse than the pain of change’? Why are the assumptions, the exhortations, based on what the seller wants? And, comically, on folks that aren’t self-identified buyers yet?
Why have sellers spent decades blaming people for not buying when they’ve ignored the processes that folks go through to bring in a new solution (so no cold feet, no laziness, no change avoidance)? After all, until they’re buyers the sales model is irrelevant for them – which explains (seller’s blame aside) the non-buying! They are not buyers yet!
SELLERS IGNORE RISKS TO STATUS QUO
I have more questions: Why is a non-purchase something to be managed by giving prospects jolts to take them beyond their alleged ‘laziness’ or ‘decision avoidance?’ What if people aren’t ‘lazy’ or ‘avoiding decisions’ but merely in a change/decision process the seller isn’t privy to?
What if the alleged ‘signs of indecision’ are a biased misreading of normal buy-in and change management practices that are not purchase-centered? What if people are NOT ‘avoiding change’ and don’t ‘prefer complacency’ or settle for ‘good enough?’
Why do sellers believe their jobs are to ‘break the gravitational pull’ and ‘beat the status quo’ rather than do something different to help them traverse their own unique decision process so they become buyers, so they understand the ‘cost’ involved with change, so everyone has bought in? Don’t sellers realize no one starts off wanting to buy anything, merely resolve a problem at the least ‘cost/risk’ to their system?
Do sellers even know what the status quo is – a unique mix of the unique people, policies, history, relationships, goals, job descriptions, etc. that make a culture operate successfully? And how, may I ask, with only ‘sales’ as their tool, would a seller know the risks to people and policies that must be managed for congruent change to happen within any unique status quo?
Why do sellers believe that prospects ‘wobble’, or ‘waiver’, or ‘back peddle’ when pushed for a close, when people (not even buyers yet!) are merely not finished getting buy-in, managing internal risks, trialing workarounds – or merely trying to get away from a pushy seller?
The term ‘decision avoidance’ has been around for decades. Sellers are warned they must ‘break the gravitational pull’ and ‘beat the status quo’. The ‘price’ issue has been an ongoing excuse. I even read this in an article recently (The Indecisive Buyer) on salesgravy.com:
“Why should anyone make a decision quickly if they don’t have to? More often than not, the buyers believe that by waiting, they will get a better deal. The salesperson will get scared and will think the only way to secure the sale is to offer a discount.”
Wait, what?
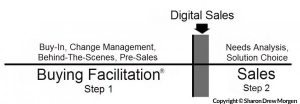
I think we should define sales as ‘A two-staged process involving facilitating the buying decision/change path, then placing solutions to those who become buyers’.
SALES ASSUMPTIONS ARE DISRESPECTFUL
There is profound disrespect inherent in all the above assumptions: Why is an entire industry so disrespectful, so eager to blame when the stubborn insistence on ONLY trying to sell (with no real knowledge as to what’s going on in the Other’s process) closes 5%, instead of recognizing that maybe something is wrong with the seller’s ‘need-focused’ assumption that there’s a ‘buyer’?
Indeed, decisions involving purchasing a solution only account for one third – the last third – of a buying decision. My clients, connecting first with Buying Facilitation® and a change facilitation focus that addresses the first two thirds of the change process, consistently close 40% against a sales-based control group that closes 5% with a ‘needs’ focus.
The very act of seeking those who seem (using biased thinking) to have a ‘need’ ignores 40% of those in process, and who will become buyers once they’re done. And as you’ll learn, it’s much, much more efficient to find prospects in the process of change than wrongly presume someone has a need and try try try to close.
And while I’m at it, why is it ok that the sales model carries an in-built, accepted, 95% failure rate? You wouldn’t even go to a hairdresser with a 95% failure rate! And an entire industry never considers that the outsized failure rate is a sign that just maybe the sales process is missing a few bits? Bits that could be discovered if they’d stop blaming people for not buying and instead look inward to recognize how they could be helping in a truly relevant way?
When I was a seller in corporate sales we said buyers were stupid. A favorite expression in the 80s and 90s was ‘buyers are liars’ (In 1992 David Sandler told me he was sorry he’d ever said that.). Sellers were told to be kind and charming, to make a personal connection, send out mass emails and play the percentages, get ‘through’ the gatekeeper. Anything to ‘get in front’ of that prospect! Anything! Assuming, of course, that once the prospect met the seller! Or heard about the product! they’d buy! Nope.
None, none of these silly excuses address what’s going on in the Buy Side!
WHEN DO PEOPLE BECOME BUYERS?
Have you ever considered that people aren’t buyers until certain benchmarks in their environment have been addressed? Sales professionals and marketers can facilitate these benchmarks. Just not with sales thinking.
The time it takes to figure out how to fix a problem in a way that causes the least risk to the system (AND there is buy-in, AND the ‘cost’ of a solution is lower than the ‘cost’ of maintaining the problem) is the length of the sales cycle. This is not indecision, a term used when
- the seller has determined a ‘need’,
- the seller believes a sale is imminent and has put the ‘prospect’ in their pipeline,
- a seller isn’t getting what s/he expects to occur,
- there’s no response to a pitch or marketing campaign,
- it’s taking ‘too long’ to close,
- the process involved in the prospect’s decision making is ignored.
Silence doesn’t mean back peddling, or complacency, or that a decision isn’t in progress. Someone recently asked me what to call people who haven’t yet become buyers. “People.” And People are who you’re blaming for not being buyers, people just trying to find excellence without disruption, without throwing the baby out with the bathwater. People who haven’t considered the option of buying anything. Yet.
People aren’t indecisive: they are going through a necessary, systemic process. It just doesn’t follow or heed the sales model. And until this change management process is complete, people will ignore sales outreach.
And yes, I recognize that the industry has used my concepts I developed 40 years ago of workarounds, buy-in, stakeholders, etc., and added them into the Sell Side, mentioning these points to would-be prospects and offering research on what Others have done to ‘beat the status quo.’
But as long as sellers continue to work in service of closing a sale instead of using a different thought process (and new skills, such as Facilitative Questions, listening for systems, etc.), with a goal to first facilitate systemic change, you’re still manipulating to get your own needs met. And people will resist you.
TWO-SIDED DATA SET
The sales model has no capability of understanding the idiosyncratic and complex issues people deal with to resolve a problem.
Potential buyers themselves have a confusing time trying to understand their full problem, something they cannot do until all the stakeholders have weighed in and the ‘cost’ of the risk involved is known. And sales folks NEVER speak with the entire set of stakeholders! (BTW using Buying Facilitation® you would!)
The truth is, using the just sales model, there is no way a seller can understand any of the challenges to change that prospective buyers face. It certainly does NOT help people assess the real risk to their system, even as they ‘paint a compelling picture of the pain of same’ with very very little real data. Not to mention actually believe they’re ‘smarter and more savvy than customers.’ (I actually heard a noted sales guru say this recently.)
Obviously, telling prospects what other companies have done to manage risk, is just silly, and another form of push sales. With no knowledge of the intricacies of a specific culture, or how the identified problem got created or maintained, there is no credible data from others that will be applicable.
And people are NOT in pain! That’s a sales word to mitigate assumptions.
EXAMPLES OF RISK IN THE BUYING DECISION PROCESS
People don’t want to buy anything, merely resolve a problem at the least ‘cost’ (risk) to their system: the ‘cost’ of a possible solution must be equal to or less than the ‘cost’ of the problem.
The status quo is maintained ONLY when the ‘cost’ of change is recognized as being higher than the ‘cost’ of the problem. If you need to fire 8 people to buy a new piece of software, which carries the most risk?
I did a pilot Buying Facilitation® (a change facilitation model I invented when I realized, as a seller-turned-entrepreneur, that the problem was in the buying process) training for Proctor and Gamble years ago. It was highly, highly successful – a massive increase over the control group. But they couldn’t train the entire sales force because it would cost $3,000,000,000 to change (new trucks and faster robots to handle the higher volume of sales, global rollouts etc.) and take two years to recoup the cost.
I did a BF pilot for Boston Scientific. Again, the pilot was massively more successful than the control group, but they thought the model was too controversial and disruptive: they’d need to change their marketing, follow-up, and customer service practices to employ it.
The pilot at Safelight Auto Glass was also highly successful. The reps made more money, closed more sales, faster. But the reps – hired to go out daily and deliver donuts (True story) as part of their ‘relationship management’ – all submitted their resignations en mass, a month after the course because they WANTED to be out in the field delivering donuts!
From the sales side, none of those stories make sense. But from the Buy Side, the cost of change was too high. They ‘needed’ my solution; they loved me and Buying Facilitation®; the companies understood that with Buying Facilitation® they made more money – a lot more money. The risk, the cost, the disruption, was too high. Nothing to do with need.
EXCUSES WHY BUYERS DON’T CLOSE
During the 43 years I’ve been teaching my Buying Facilitation® model I’ve heard bazillions of excuses that blame buyers, all from the Sell Side. But it doesn’t need to be this way.
See, buyers must do this anyway, with you or without you. By using only the sales model, you can only sell to those who show up as buyers. By adding change facilitation, you can enter at the beginning, facilitate them (with a change/leadership lens NOT a solution-placement lens) through to being ready to buy, THEN sell to people who are real buyers.
And with a change facilitator’s hat on, you can easily discover would-be buyers ON THE FIRST CALL that you can’t do with a sales hat on.
With my 7 books and hundreds of articles on facilitating buying, I’ve been describing how buyers buy, including recent articles on the Buy Side vs the Sell Side, and buyING vs BuyERS.
THE 13 STAGES OF THE BUYING DECISION PROCESS
There are two elements to the buying process:
- The change management end – where potential buyers reside and standard sales outreach doesn’t reach (they’re not self-identified as buyers yet);
- The purchasing end.
Sales does a great job with #2. By ignoring #1, you’re left pushing to ‘overcome indecision.’ But there’s no indecision: they’re just not ready yet.
Let me explain what’s going on. Decisions, including a buying decision, are just not so simple as weighting options. It’s about risk to the culture, the environment, the people, the norms, the jobs – the status quo. Risk avoidance (or maintaining Systems Congruence as systems thinkers call it) is a vital component of all decision making.
For our purposes, let’s call this change management process a buyING process. It includes 13 stages (written about extensively in my book Dirty Little Secrets):
- Idea stage: Is there a problem? Who needs to be involved to gather the full fact pattern?
- Brainstorming stage: Idea discussed broadly with colleagues.
- Initial discussion stage: Initial group of chosen colleagues discuss the problem to gather full fact pattern: how it got created/maintained; posit who to include on Buying Decision Team; consider possible fixes and fallout. Action groups formed to bring ideas for possible workarounds to next meeting. Invites for new, overlooked stakeholders to join.
- Contemplation stage: Workarounds (previous vendors, inhouse solutions) discussed for efficacy. People who will touch a solution to discuss their concerns to engage before they resist. More research necessary on possible solutions, ways to determine viable workarounds.
- Organization stage: Group gathers research to discuss upsides and downsides of workarounds. Viability of workarounds determined.
- Change management stage: If workarounds acceptable, group goes forward to plan to implement. If workarounds deemed unacceptable, group begins to consider downsides of external solutions: the ‘cost’(risk) of change, the ‘cost’ of a fix, the ‘cost’ of staying the same, and how much disruption is acceptable. Broad research for next meeting on solutions that might meet the criteria and ‘cost’ minimal disruption.
- Coordination stage: Dedicated discussions on research in re risk factors, buy-in issues, resistance. Delineate everyone’s thoughts re goals, acceptable risks, job changes, and change capacity. Must consider: workaround vs purchase vs status quo; decide on partial fix vs complete fix; decide on time criteria. Folks with resistance must be heard and group to decide how to include and dismantle resistance. Specific research to be assigned based on decisions reached. Discussions on next steps.
- Research stage: Discussion on research that’s brought in for each possible solution. Who is onboard with risk? How will change be managed with each possible solution? To include: downsides per type of solution, possibilities, outcomes, problems, management considerations, changes in policy, job description changes, HR issues, etc. and how these will be mitigated if purchase to be made – or discussion around maintaining the status quo instead of resolving the problem at all (i.e. cost too high). If a purchase is preferred option, list of possible types of solutions to purchase now defined; research for each to be ready for next meeting.
- Consensus stage: Known risks, change management procedures, buy-in and consensus necessary for each possibility. Buying Decision Team makes final choices: specific products and possible vendors are named. Criteria set for solution choice.
- Action stage: Responsibilities apportioned to manage the specifics of Step 9. Calls made to several vendors for interviews, presentations, and data gathering. Agreed-upon criteria applied with each vendor.
- Second brainstorming stage: Buying Decision Team discusses results of calls and interviews with vendors and partners, and fallout/benefits of each. Favored vendors pitched by team members among themselves, and then called for follow on meetings.
- Choice stage: New solution/vendor agreed on. Change management issues that need to be managed are delineated and put in place. Leadership initiatives prepared to avoid disruption.
- Implementation stage: Vendor contacted. Purchase made. Implement and follow on.
These comprise the complete decision path that everyone goes through before self-identifying as buyers. Notice they don’t begin considering buying until Stage 9 when they have their ducks in a row! Until then they’re only people trying to fix a problem at the least risk to the system. 40% of these people will be buyers once they complete their process.
Until then they’re merely People trying to solve a problem! The sales model is useless here! And there is no indecision.
SELLING IGNORES BUYING
Sales don’t close because of sales process only attracts the low hanging fruit who have completed their stages and show up as self-identified buyers. A buying decision starts of as systemic:
- Until everyone (all stakeholders who touch the current problem that needs resolving) adds their thoughts into the mix there is no way to fully understand the problem (and it follows, no way to consider a possible resolution). Sometimes it takes a period of time to recognize the full set of stakeholders. It’s certainly not as simple as it seems. Must they include ‘Joe in Accounting’? HR? Often stakeholders show up late in the decision process and the entire process must start from the beginning or face irreparable disruption.
- Until all workarounds are tried, until old vendors, other departments, friends and referrals are found and studied, outside solutions (i.e. purchases) will not be considered regardless of need or the efficacy of a specific solution. Any marketing materials or sales discussions will be ignored until internal fixes are found to not be viable.
- Until the full ‘cost’ (risk) of a proposed fix is understood and found to be less than the ‘cost’ of maintaining the status quo (i.e. cheaper than dealing with the originating problem), no action will be taken; the risk of disrupting the system is too great.
- Until the ‘cost’ is deemed manageable, AND the full set of stakeholders who will touch the final solution is on board, AND the team buys-in to any change involved, there will be no purchase and the status quo will be maintained.
And there can be no decision to purchase anything until completed.
NO ONE WANTS TO BUY ANYTHING
I’ve taught 100,000 clients Buying Facilitation® to use as a front end to sales. With specific questions (I invented a new form of question for this) we seek folks going through change in the area my solution supports – those who WILL become buyers instead of seeking those who have already self-identified and can use your website to get what they need.
No, you can’t use the sales model for this. Yes, you’ll need an additional tool kit; Buying Facilitation® uses Facilitative Questions, systems listening, the steps of change, and a commitment to facilitating systemic change before trying to sell anything. Read dozens of articles I’ve written on the subject.
Maybe it’s time to make Buying Facilitation® your new new thing, put the onus of blame on the restrictive sales model, and go beyond merely placing solutions – and actually sell more. This is what people REALLY need help with! They know how to find you, and how to buy once they get there. Help them get there.
Remember: you have nothing to sell if there is no one to buy.
__________________________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen June 12th, 2023
Posted In: News
Questions Aren’t All They’re Cracked Up To Be

Ask more questions! sellers are admonished. Ask better questions! leaders and coaches are reminded. Questions seem to be a prompt in many fields, from medicine to parenting. But why?
There’s a universal assumption that questions will yield Truth, generate ‘real’ discussion topics or realizations, or uncover hidden gems of information or important details. Good questions can even inspire clarity. Right?
I’d like to offer a different point of view on what questions really are and how they function. See, I find questions terribly subjective, don’t enable Responders to find their real answers, and often don’t get to the Truth. But, it’s quite possible to use questions in a way that enables Others to discover their own, often hidden and unconscious, answers.
WHAT IS A QUESTION?
Let me start with Google’s definition of ‘question’: a grouping of words posed to elicit data. Hmmmm…. But they don’t often elicit accurate data. Here’s my definition. Questions are:
- posed according to the needs, curiosity, goals, and intent of the Asker;
- interpreted uniquely and unconsciously, according to a Responder’s world view;
- potentially ignore more important information outside the Asker’s purview.
And, to make it worse, our normal processes get in the way:
- Language: Questions are posed using words and languaging unique to the Asker. Using their own (subjective) intent and goals, their own idioms and word choices, Askers assume Responders will accurately interpret them and respond along expected lines. This expectation is most easily met between folks who are familiar with each other, but less successfully with those outside the Asker’s sphere of influence. Too often Responders interpret a query quite differently than intended, offering responses far afield from the Asker’s intent.
- Listening/brain: All incoming words enter our ears as meaningless sound vibrations (see my book WHAT? on this topic), “puffs of air” that eventually get translated according to historic circuits based on our mental models that have been set during our lifetimes. In other words, and similar with the language problem, Responders may not accurately translate incoming questions according to the intent of the Asker. The way Responders hear and interpret the question is at the mercy of the Responder’s brain circuits.
- Curiosity: Often an Asker seeks data, thoughts, according to his/her desire for knowledge. It might be for research, interest, or ego – to exhibit their intelligence or prove their commitment. Yet given the way information is stored and retrieved in the brain, the question may capture some degree of applicable data, or a whole lotta subjective, unconscious thoughts that may or may not be relevant.
As you can see, questions posed to extract useful, relevant data have a reasonable chance of failure: with an outcome biased by the needs and subjectivity of the Asker, with Responders listening through brain circuits that delete incoming sound vibrations and only translate incoming words according to what’s been heard before, it’s likely that standard questions won’t gather the full set of information as intended.
TYPES OF QUESTIONS
Here’s my opinion on a few different forms of question:
Open question: To me, open questions are great in social discussions but there’s no way to get precise data from them. What would you like for dinner? will prompt an enormous variety of choices. But if the fridge only has leftovers, an open question won’t work, and a closed question “Would you like me to heat up last night’s dinner or Monday night’s dinner?” would. Open questions cause brains to do a transderivational search that may unearth responses far afield from the Asker’s intent and the Asker is out of control.
Closed question: I love these. They are perfect when a specific response is needed. What time is dinner? Should we send answers now or wait until our meeting? Of course they can also be highly manipulative when only limited responses are offered for potentially broad possibilities.
Leading question: Don’t you think you rely on conventional questions too much? That’s a leading question. Manipulative. Disrespectful. Hate them.
Probing question: Meant to gather data, these questions face the same problem I’ve mentioned: using the goal, intent, and words of the Asker, they will be interpreted uniquely as per the Responder’s historic stored content, and extract some fraction of the full data set possible.
Given the above, I invented a new form of question!
FACILITATIVE QUESTION
When I began developing my brain change models decades ago, I realized that conventional questions would most likely not get to the most appropriate circuits in someone’s brain that hold their best answers.
Knowing that our brain’s unconscious search for answers (in 5 one-hundredths of a second) leads to subjective, historic, and limited responses along one of the brain’s neural superhighways, I spent 10 years figuring out how to use questions to help people find where their unbiased (and unconscious) answers reside.
One of the main problems I had to resolve was how to circumvent a brain’s automatic and unconscious preferences to make it possible to notice the broadest view of choices.
Language to avoid bias and promote objectivity
Since questions (as words) are automatically sent down specific neural routes, I had to figure out a way to use language to broaden the routes the brain could choose from, expand possibility, and circumvent bias as much as possible – a difficult one as our natural listening is unwittingly biased.
Incoming words get translated according to our existing superhighways that offer habitual responses. To redirect listening to where foundational answers are stored, I figured it might be possible to use questions to override and redirect the normal routes to find the specific cell assemblies where value-based answers are stored and not always retrieved by information gathering questions! That led me to a model to use specific words in a specific order so the brain would be led to find the best existing circuits.
To accomplish this, my Facilitative Questions are brain-change based, and save information gathering until the very end of the questioning process when the proper circuits have been engaged.
Getting into Observer
To make sure Responders are in as neutral and unbiased a place as possible, avoid the standard approach of attempting to understand, and have a chance of listening without misunderstanding, Facilitative Questions are formulated in a way that puts Responders in Observer, a meta/witness position that overrides normalized neural circuitry. They are not information gathering and use the mind-body connection to direct incoming messages to where accurate answers exist that often are not noticed via conventional questions.
Let me show you how to put yourself into an Observer, coach/witness position – the stance you want your Responders to listen from – so you can see how effective it is at going beyond bias. You’ll notice how an objective viewpoint differs from a subjective one and why it’s preferred for decision making. Indeed, it’s a good place to listen from so you can hear responses without your own biases.
Here’s an exercise: See yourself having dinner with one other person. Notice the other person across from you (Self, natural, unconscious, subjective viewpoint). Then mentally put yourself up on the ceiling and see both of you (Observer, conscious, objective, intentional viewpoint).
If you’re having an argument with your dinner partner, where would you rather be – ceiling or across the table – to understand the full data set of what was going on so you could make personal adjustments?
On the ceiling, where you’d see both of you. From this meta position, you’d be objective, free from the feelings and biases that guided the argument along historic circuits. From Observer you’d have the best chance to make choices that might resolve your problem. Try it for yourself! Don’t forget to go back down to Self to communicate warmly. My clients walk around saying ‘Decide from Observer, Deliver from Self.’
So when developing Facilitative Questions, I had to put listeners into Observer. I played with words and found that these cause Responders to unconsciously step back (i.e. meta) to look into neural circuits with an unbiased, less subjective, and broader view.
- how would you know if…
- what would you need to understand differently…
Notice they immediately cause the Responder to ‘observe’ their brain; they do NOT gather data or cause ‘understanding’ in the Asker. The intent is to have the Responder begin to look into their brains to discover answers stored outside the automatic circuitry.
Change the goal
I also had to change the goal of a question, from my own curiosity and need to elicit data to helping the Other discover their own answers. Instead of seeking to understand, have the goal of facilitating Responders to their own data sets stored in different places in their brains, places not accessible to Askers using conventional questions. After all, their systems are so unique that an outsider couldn’t know the answers anyway.
Here’s an example of a standard question, biased by the needs of the Asker:
“Why do you wear your hair like that?”
puts the Responder directly into Self and their automatic, historic, unconscious responses, while
“How would you know if it were time to reconsider your hairstyle?”
is a Facilitative Question that uses specific words that cause the Responder to step back, look into their full circuitry involving hair (How would you know), consider current and past hairstyles (if it were time), note their situation to see if it merits change (reconsider), and have a more complete data/criterion set with which to possibly make a change – or not.
Note: because some questions are interpreted in a way that (unwittingly) causes Responders to distrust you, Facilitative Questions not only promote an expanded set of unbiased possibilities, but encourages trust between Asker and Responder and doesn’t push a response.
Questions follow steps to change
The biggest element I had to figure out was the sequence. I figured out 13 sequential steps to all change and decision making and I pose the Facilitative Questions down the sequence. Here are the main categories:
- Where are you and what’s missing? Responder begins by discovering their full set of givens, some of which are unconscious.
- How can you fix the problem yourself? Systems don’t seek change, merely to resolve a problem at the least ‘cost’ to the system. To minimize any ‘cost’ involved, it’s best to begin by trying to fix the problem with what’s familiar.
- How can you manage change without disruption and with buy-in? Until it’s known what the fallout of the ‘new’ will be, and there’s agreement, no change will occur.
WHEN TO FACILITATE UNBIASED DISCOVERY?
Facilitative Questions are especially helpful in
- data gathering to discover a more expanded range of choices,
- decision making to uncover each element of consideration as matched with values and outcomes,
- habit/behavior when seeking to understand and modify the patterns and neural circuitry underlying the current behaviors,
- leadership, sales, coaching when leading others to discover routes to new choices.
I’ve trained these questions globally for sales folks learning my Buying Facilitation® model to help prospects become buyers, and for coaches and leaders to help followers discover their own best answers.
If your job is to serve, the best thing you can offer others is a commitment to help them help themselves. Facilitative Questions can be used in any industry, from business to healthcare, from parenting to relationships as tools to enable discovery, change, and health.
It takes a bit of practice to create these questions as they aren’t natural or curiosity based, but the coaches, sellers, doctors, and leaders I’ve taught them to use them to help Others discover their own excellence, avoid resistance, and maintain trust between the Asker and Responder. I encourage you to consider learning them. And I’m happy to discuss and share what I know. sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com My hope is that you’ll begin to think about questions differently.
___________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen June 5th, 2023
Posted In: News
Influencers Must Change Brains, not Minds: why information, persuasion, and motivation don’t cause change

As an influencer, how often do say to yourself “Why doesn’t she understand me?” or “If he understood me better this decision would be a no-brainer.” It’s natural to assume Others will understand – and comply with – your suggestions. Have you ever wondered what’s happening when they don’t?
As an influencer, part of your job is to facilitate change. But how? In general, you’ve likely used great rationale, logic, and leadership, data sharing, or just plain directives. But what if your Communication Partner’s brain isn’t set up to hear you accurately? What if your words are misinterpreted, or not understood? You naturally assume your words carry the meaning you intend to convey. But do they?
Sometimes people misinterpret you and your audience is unintentionally restricted to only those who naturally understand your message. Sometimes people ignore you, regardless of how important your message, how engagingly you deliver it, or how badly they need it.
What if ‘changing minds’ is the wrong way to think about it, and if your real job is to ‘change brains’? What if the Other’s brain, it’s neural circuitry, was in charge and your job was to facilitate the way it went about decision making?
OUR BRAINS ARE THE CULPRIT
Thinking about using any form of content-based sharing as a persuasion strategy, let me share a confounding concept: words have no meaning until our brain interprets them. According to John Colapinto in his fascinating book This is the Voice,
Speech is a connected flow of ever-changing, harmonically rich musical pitches determined by the rate at which the phonating chords vibrate, the complex overtone spectrum is filtered by the rapidly changing length and shape of the mouth, and lips, interspersed with bursts of noise…It is our brain that turns this incoming stream of sonic air disturbances into something meaningful. (pg 54)
Seems to parallel how we ‘see’ color. We don’t, exactly. Light vibrations enter our eyes and get translated into color by our rods and cones. Otherwise, the world is gray! Indeed, both what we see and what we hear are largely out of our control, influencing what we notice (or not), how we decide (or not), what we think and hear and are curious about (We can’t be curious unless we have the circuitry to think with!).
Here’s a greatly simplified explanation of how brains translate incoming words (or sounds, or…) as I learned when researching my book WHAT?: Spoken words, like all sounds, are merely meaningless electrochemical vibrations that enter our ears as ‘puffs of air’, as many neuroscientists call the vibrations, that get filtered, then automatically dispatched as signals to what our brain considers a ‘similar-enough’ circuit (one among 100 trillion) for translation. And where the signals don’t match, a Listener’s brain kindly discards the difference!
People understand us according to how the selected circuits translate these signals, regardless of how different they are from the intended message.
In other words, people don’t hear us according to what we say but by how their historic circuitry interprets it. To me this is quite annoying and hard to address: not only does that restrict incoming content to what’s already familiar to us, there’s a chance that what we think was said is only some fraction of what was intended.
Unfortunately, neither the Speaker or Listener understands how far from accurate the translation is. Listeners assume their brains tell them exactly what’s been said; Speakers assume they’ve been heard accurately. Turns out these assumptions are both false; communication potentially ends up biased, restricted, and subjective.
THE BRAIN/INFORMATION PROBLEM
The misinterpretation problem gets exacerbated when words get sent down circuits that unwittingly incur resistance, as Others ‘hear’ something that goes against their beliefs. If my brain tells me you said ABL it’s hard to convince me you said ABC. I’ve lost friends and partners that way and didn’t understand why until my book research. And sadly, it all takes place outside of conscious awareness.
This is especially problematic when there’s a new project to be completed, supervision to correct a problem, or Business Process Management to be organized. It’s a problem between parents and teenagers and a curse in negotiations. As leaders, without knowing how accurately we’re heard, we have no idea if our directives or information sharing is being received as we intend.
This possibility of misinterpreting incoming words makes the case for providing information when it can be most accurately translated: when the Listener knows exactly what they are listening for, the brain has a more direct route to the appropriate circuits to interpret them.
In other words, instead of starting with goals or solutions for Others, we need their direct buy-in first. To invoke change, help Others figure out what they need from you then supply content that will be applied accurately. In other words, instead of shooting an arrow to hit a bullseye, first shoot the arrow then draw the bullseye where the arrow lands!
INFORMATION IS LAST
After 60 years of studying, and developing models for, systemic brain change and decision making, I’ve realized that offering ideas, directives, suggestions, or information is the very last thing anyone needs when considering doing something different (i.e. buying, changing habits, etc.). And yes, it goes against most conventional thinking. But hang with me.
As a kid, my then-undiagnosed Asperger’s caused me to act differently than people around me. I was in trouble often and never understood why. I began reading voraciously on how to change my behaviors: how to visualize, to motivate myself, be disciplined. But they were all based on trying to fix my seemingly automatic actions, to change my behaviors. And I failed repeatedly to make any of the changes permanent.
I finally acknowledged it’s not possible to change a behavior by trying to change a behavior, my brain was the culprit. I then began developing neural workarounds to:
- create new brain pathways to new behaviors,
- consciously change the circuits causing my behaviors,
- enhance my ability to translate incoming words accurately.
I know, I know. It’s odd, and there was lots of trial-and-error. But eventually I figured it out and dedicated the rest of my life to developing, writing about, and teaching systemic brain change models for conscious behavior change.
Thankfully, my concepts caught on in sales, coaching, leadership, and change management: my facilitation models help people orchestrate their own change based on their own internal norms, values, and criteria: in sales, my Buying Facilitation® model teaches people on route to fixing a problem how to become buyers. In coaching and change management, I provide the skill sets to enable people to discover, and act on, their own unique criteria and avoid resistence.
CHANGE FACILITATION
For those of you whose job is to get Others to do something you want them to do, let’s look at it from the side of the people you seek to change.
In order for change to occur, people must understand the difference between their status quo (their problem) and the new activity you want them to do. Below are all the specific factors they must address to be ready, willing, and able to change:
Conform to norms: Change is more than doing something different; it demands a reconfiguration of the brain circuitry. And it’s only when an incongruence is noticed that something different is required. By first facilitating people through their discovery – by leading them to the underlying beliefs and values that created the circuits that caused the problem – they can discover an incongruence and be willing to change. It’s got nothing to do with new content or imposed regulations, regardless how important they are. I created a new form of brain-directive question (i.e. not information gathering) called a Facilitative Question that’s quite effective at leading others to their own, often unconscious, answers.
Cost: It’s not until the ‘cost’ (resource, results, disruption) of a fix is identified and agreed to by all stakeholders (including mental models and beliefs) that it’s possible to know if a problem is worth fixing. No one naturally seeks out change if all seems fine, regardless of the problem or the efficacy of the solution.
Disruption: Because our internal systems seek balance (homeostasis), we avoid disruption. And the time it takes us to find a route through to a change that matches our values and avoids risk is the length of the change cycle. If new behaviors are required that cause someone to be out of balance, they will be resisted.
Personal: When change is sought, people must discover their own route to change that match their values and maintains homeostasis. And outsiders can ever understand someone’s history, values, norms, or neural configurations.
EACH PERSON MUST DESIGN THEIR OWN CHANGE
To facilitate change efficiently, we need a shift in thinking. Instead of trying to have the answers for Others, first focus on the goal of helping Others discover how to handle their own change issues; enable them to discover their own incongruences. Then they’ll know exactly where they need to add or subtract something to fix it, and the influencer can supply the information to complete the process.
Here’s a situation where I used a carefully crafted sentence to direct a friend’s thinking to where her choice points lie.
I have a lovely young friend who, to me, had serious energy problems. Some days she had difficulty getting out of bed, even with 5 children. Some days she didn’t have the energy to cook or work. And she’d been having this issue for decades. After knowing her a year I finally said, “If the time ever comes that you wish for additional choices around your store of energy to be more available for your kids, I have a thought.”
By shifting the context to her children, by giving her control over her choices and not trying to change her, by leading her to each of her decision points, her system didn’t feel threatened. She welcomed my thoughts, got help (My naturopath discovered she was actually dying from a critical lack of vitamin B12.) and now is awake daily at 5:30 a.m. with endless amounts of energy.
No matter what the problem or solution may be, unless someone understands that change won’t cause major disruption, unless the new fits with their values and criteria, unless all the people involved agree to change, they won’t consider doing anything different. So how can we help Others find their own excellence?
13 STEPS TO CHANGE
You must begin by trusting Others have their own criteria for change. Instead of starting with answers or goals, lead them down their unique path through to discovery, to notice any incongruences they can’t resolve on their own. Then they’ll know exactly what they need from you and be ready to hear your information. And as you’ve already helped them help themselves, they’ll come to you for their needs and trust has been established when you offer them new ideas.
The facilitation model I developed leads buyers, teams, coaching clients through to discovery. It involves 13 specific steps that follow the sequence all brain change takes as a precursor to behavior change, providing the tools to help the Other figure out their own path. By then they’ll need your information. To address change congruently, people must first:
- recognize the full set of givens involved;
- identify and include all stakeholders, beliefs, criteria, and norms;
- try workarounds to fix the problem internally if possible;
- understand and accept the risk of change;
- get buy-in to adopt the new.
It’s not so simple as an outsider gathering or sharing information or posing questions to help the influencer understand. Because until they know that the cost change will be equal to or less than their status quo, they will not take action.
Historically, I’ve taught this facilitation process successfully to 100,000 sales professionals and coaches. But with the new technology, it’s quite possible to use it in marketing for Deal Rooms, ABM discussions, and Sales Enablement.
So as you consider delaying your storytelling or pitching until you’ve facilitated change, ask yourself:
- Would you rather speak or be heard?
- What is your job – to serve Others through to their own form of excellence or get your point across to anyone who can listen?
- Do you seek a quick hit or a long-term relationship?
- Would you rather be a servant leader or an information hawker?
You decide. It’s possible to serve Others and be available with information when and as they need. Sellers can first facilitate buying, coaches and facilitate permanent change, and marketers can develop content that leads people through to brain change. I’m here if you have questions. Or go to www.sharon-drew.com to learn about my facilitation and brain change models.
_______________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen May 8th, 2023
Posted In: News
Thank You. We Appreciate You: a case study in caring for employees
 Early this morning I went to my favorite ‘big box’ supermarket, WinCo. If you’re not in one of the 5 states where it operates (Washington, Idaho, Nevada, California, and Oregon), you may not be familiar with it and I’d like to introduce you. WinCo is an employee-owned food-supply chain that cares as much for its employees as it does for its customers. As a result, the customer service and store care is exceptional: the stores are spotless, well-stocked, and employees are easy to find if you have a question, not to mention always kind, informed, and personal. And it’s always a surprise to find items I purchase in more specialty stores – even Amazon! – at least 40% cheaper! Who knew my favorite Roasted Salsa Verde (Herdez) was available at half the price! I love this store and am willing to drive out of my way to shop there. As I was walking down an aisle I noticed a tall woman and young man walk over to a much older man as he was cleaning the floors:
Early this morning I went to my favorite ‘big box’ supermarket, WinCo. If you’re not in one of the 5 states where it operates (Washington, Idaho, Nevada, California, and Oregon), you may not be familiar with it and I’d like to introduce you. WinCo is an employee-owned food-supply chain that cares as much for its employees as it does for its customers. As a result, the customer service and store care is exceptional: the stores are spotless, well-stocked, and employees are easy to find if you have a question, not to mention always kind, informed, and personal. And it’s always a surprise to find items I purchase in more specialty stores – even Amazon! – at least 40% cheaper! Who knew my favorite Roasted Salsa Verde (Herdez) was available at half the price! I love this store and am willing to drive out of my way to shop there. As I was walking down an aisle I noticed a tall woman and young man walk over to a much older man as he was cleaning the floors:
Woman: We’d like to give you a gift (She handed him an envelope – I assume it was a check.) for all the hard work you do and how well you take care of us all. You always go the extra step to make this store even better. We deeply appreciate you and all do you for us. We all thank you.
I must admit I stopped in my tracks and began crying a bit. I had never heard this in any store, nor have I been aware of supermarkets gifting and thanking employees for their service. I sought the woman (his manager?) out.
SD: Do you choose an ‘employee of the month’ each month and hand out checks to the winners?
Woman: No. It’s on an individual basis. Sometimes we hand out a few in one month, sometimes only a few a year. It depends. When we notice someone doing a great job we reward them and let them know they’re important to us. It’s pretty simple. We take care of each other and show our appreciation when one of us shines.
‘We take care of each other’. So simple! When was the last time you let an employee, one of your staff or team, know how much they were appreciated? Went out of your way to take care of them? OUR EMPLOYEES ARE OUR FIRST CUSTOMERS When I started up my tech company in 1983 in London I had never run a business before. But even without knowing ‘the rules’ I knew it was as important to care for my team as well as I cared for clients. To that end I put in place some initiatives to make sure they felt taken care of. Every year I gave the management team a fully paid week off and a $3,000 check for tuition and travel to take any type of course they wanted (Photography? Pottery?), even if the subject matter had nothing to do with their jobs. The goal was to help them keep their brains creative and curious. Certainly a way to let them know I appreciated them. I also didn’t give them vacation time per se but told them to take off whatever time they needed (so long as they covered their responsibilities) when they felt they weren’t operating on all cylinders. I told them I trusted them to know when they needed rest – it wasn’t about the time. Surprisingly I had to force them to take time off. I would call their wives – and in those days (1980’s) the team was mostly men and the women were usually at home doing child care – tell them to give the kids to the grandparents for a few days, and keep their husbands in bed. To make sure they had plenty of time to relax, I had restaurants deliver food to them so no one had to cook or shop. My folks would return rested with happy faces. Because it was quite important to me that we all meshed even though in scattered locations, I took my inside and outside folks to a pub once a month for beer and darts. I always lost (I never figured out darts in all my years in London!); out of pity, I suspect, they then bought the next round. FIELD FOLKS BROUGHT IN BUSINESS To keep abreast of the field folks (the techies) and make sure they felt like part of the company, I called each of them once a month to check in. Sure, I only had 40 people in the field so it was doable (My secretary would schedule the calls to make sure we connected). One of the pluses of my check-ins was they would tell me when our client was preparing to upgrade the program/package we supported. I knew the vendor had a team that installed it, but that would have taken business away from us and we could easily do the installation. I certainly wanted to be involved with any follow-on work. I would then call my client before the new software was installed and asked if they’d be willing to continue working with us if they brought in new software. Of course they were happy to have us do the work, given my staff’s excellence. This factor alone caused my business to explode. I once even got a call from the vendor: “You’re killing me. Clients order an upgrade but don’t hire us to do any programming because you’re already handling it. How do you get in there so fast?” My colleagues chided me when they found out how well I took care of my peeps: “Are you running a spa?” they’d ask. “Don’t you think your folks will take advantage?” I think they were jealous, but that didn’t stop them from trying to hire my staff away from me. I would hear grumbles at conferences, gossip that they were offering big bucks to lure my folks away. But nope, I never lost an employee to anything other than relocation in four years. They were happy. Together we grew the business from zero to almost $5,000,000 in under four years – with no internet (1984 -1988), no websites, no email, no Twitter, no LinkedIn. Just me – a rookie entrepreneur – and my team remained dedicated to caring for our clients and each other. WHO IS YOUR CLIENT? I believe our employees are our first customers – happy staff happy clients. Why do we forget this? How is it possible that some of the larger companies are known to have high turnover, low pay, and very strict hours with rules designed to minimize variance and kill the creative spirit rather than maximize kindness and respect? Why are companies willing to harm employees, to be disrespectful and unkind, just to save a buck? When did money become more important than values or humanity? What are they saving, anyway? When I did consulting work at KPMG I noticed a bravado about working all night, or 80 hour weeks. No surprise that many of the partners were on their third marriages – almost all on their second. Working that hard – hard enough to ignore sleep, relationships, food – was a highly valued part of the culture. Why? Why don’t we take care of our employees better? Trust them and their ideas? Take time to listen to them? Make them understand that without them we can’t be successful? How did people become expendable to save money at all costs? I know a very large, successful multinational that forces all levels of employees to spend hours preparing for meetings with senior managers where they’d have to make a case to receive modest funds – even $200! – for an online skills course or money for needed coaching. It’s a misuse of everyone’s time, disrespectful, and not even rational. Why not give mid-level managers a slush fund to have on hand when someone needs something and trust their judgement!? Why not hire people you can trust and let them decide what their folks need? We all put so much energy into our clients and customers so we can make money. Why don’t we offer our staff the same respect? We spend a fortune hiring and training the ‘right’ people and then create rules and restrictions to control them. We treat them like chits, like cogs in a wheel and make them replaceable, ‘things’ without value. And yet we want them to deliver for us and complain about turnover, about their lack of ownership. What we lose is not only ideas and loyalty, but the spirit of a man, the heart of a woman. We too often make our employees objects. I’ve interviewed middle managers in large corporations who tell me they’ve stopped bringing in new ideas because they don’t get heard, or live only for their vacation time because they’re so miserable and stay only because they’re getting paid so well. Let’s take as good care of our employees as we do our clients and customers. Let’s make sure everyone is given the time, the respect, the remuneration, to work in an environment that is filled with kindness, trust, creativity, collaboration and ideas so they can’t wait to come to work each day. Let’s treasure each of our employees. They are, indeed, special. That’s why we hired them. What’s the cost? What’s the cost if we don’t?
__________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen May 1st, 2023
Posted In: News
Servant Leadership: new skills to serve others, and why the old ones don’t work
 I became enamored of the concept Servant Leadership in the 1980s. Developed by Robert Greenleaf, it’s defined thus: a philosophy and set of practices that enriches the lives of individuals, builds better organizations and ultimately creates a more just and caring world. Greenleaf says, “The servant–leader is servant first… It begins with the natural feeling that one wants to serve.”
I became enamored of the concept Servant Leadership in the 1980s. Developed by Robert Greenleaf, it’s defined thus: a philosophy and set of practices that enriches the lives of individuals, builds better organizations and ultimately creates a more just and caring world. Greenleaf says, “The servant–leader is servant first… It begins with the natural feeling that one wants to serve.”
I’ve developed some tools to help enable the delivery of Servant Leadership in our actions.
THE BIAS PROBLEM
As a Quaker, I deeply believe that serving one another is a necessary aspect of our lives. But sometimes, especially in a business setting, standard communication skills don’t make it easy for influencers to truly serve:
- Conventional questions are little more than interrogations based on the needs/biases of the Asker, thereby restricting the full set of possible responses. Obviously this causes flawed data gathering, missed opportunities, resistance, loss of success, and damaged relationships.
- With our subjective listening filters, biases, assumptions, triggers, and habituated neural pathways, normal listening restricts us to hearing mainly what our brains want us to hear. Obviously, our range of understanding is restricted accordingly.
- Information – regardless of its accuracy, importance, or presentation – cannot be accurately interpreted due to the way our brains translate incoming sound vibrations. In other words, even though we share information as a way to help, we have no way of knowing whether or not it will be understood as we hope, misunderstood, or rejected if it seems to fly in the face of the Other’s unconscious Beliefs. It’s just not possible for information gathering or sharing to elicit permanent change, regardless of its efficacy.
- Influencers tend to focus on Behavior Change, forgetting that Behaviors are merely translations, the visible expression of our Beliefs – Beliefs in action if you will. If we shift our goal to enabling Others to change their own unconscious Beliefs, their Behavior will automatically change. And we will have served them.
- Too many influencers (coaches, parents, sellers, leaders, etc.) seek to push their agendas using convincing, manipulating, explaining, advising, etc. strategies meant to influence, manipulate, modify, correct, what we think Others should do, causing resistance in all but a few.
With our current skill sets, we end up pushing our own agendas (in the name of the Other, of course), according to our subjective needs, Beliefs, and goals (using our ‘intuition’ to tell ourselves we’re ‘right’) and restrict the full set of possibilities, ignoring the Other’s unique choices and triggering their resistance.
We assume that we have the moral high ground, that because our intention is honorable, the only missing piece is ‘how best’ to get Others to do what we think they should do.
I once ran a Buying Facilitation® training for The Covey Leadership Center. They staunchly believed that because they were teaching The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People, they had the right to push and manipulate.
We forget that by assuming we have Another’s answers we end up taking their power away, assuredly biasing the direction of their growth journey, restricting their full set of choices and not serving them at all. When this causes resistance we blame them – prospects seem ‘stupid’, patients ‘don’t care’ about their health, students ‘don’t want’ to learn, and clients ‘won’t listen’ to us – for resisting.
WHY WE CAN’T CHANGE OTHERS EVEN WITH GOOD MOTIVES
We know someone needs to stop smoking, or eat differently. We are certain the environment is in trouble. People buy assault weapons that kill children. We know these behaviors are bad for us, for each other, for the world. But we don’t seem to have the ability to get Others to change. We provide scientific evidence, relate a story of someone who has died, or offer different approaches to stop. We know that a company or group really, really needs our solution. And yet they persist with failing results rather than change.
What is going on? Why would anyone prefer to maintain failure rather than change? Seems that way, but it’s not entirely accurate. Everyone would prefer Excellence, but conventional practices do not effectively manage the unconscious that would need to buy-in to, and accommodate for, any change.
Let’s start with our attempts to have Another change a behavior. Our failures are due to the ways our brains have created and maintained our status quo:
- Threatening the system: Brains contain 86 Billion neurons and 100 Trillion synaptic connections set up make decisions from, and maintain our status quo – our Mental Models, our unique ‘system’ of rules, Beliefs, values, experiences, culture, etc. – which becomes habituated and normalized over time. This system has developed our Behaviors that make it possible for us to show up every day being who we are. We wake up daily and maintain who we were yesterday, without judgement. Our system just IS, good or bad, right or wrong. And it will fight to the death to maintain itself. Literally. It’s our Identity.
- Change Behaviors: Behaviors are merely Beliefs in action. They arise from neural circuitry that electrochemically prompt specific actions to match a Belief. When we try to change nothing but the Behavior represents, when we fail to include the inherent Beliefs that a Behavior, we unwittingly push against the entire system and it will revolt. Regardless of the efficacy of a different solution or a dire need, unless the change comes from the within the system (i.e. not an outsider’s brilliant suggestions), unless the new matches our Beliefs and the system is reorganized around the ‘new’, it will be resisted. I’ve developed a change program for those seeking congruent and permanent change.
- Information doesn’t get heard: Our brains/ears hear subjectively, automatically and unconsciously filtering out and misconstruing what’s not comfortable, failing to tell us that what we think we hear is most likely some fraction ‘off’ of what the Speaker intended.
- Ignore the steps to change: As outsiders, we too often use our intuition and professed knowledge to push the change we want. But for any change to occur, for the Other’s Beliefs to shift in a way that causes Behaviors to change, the system must take specific, albeit unconscious steps: to include the change into normal operating procedures, end up with minimal disruption, and achieve buy-in.
In other words, just providing good information, just wishing to provide a way for Others to be ‘better’, will not cause them to change their Behaviors.
HOW INFLUENCERS CAUSE RESISTANCE
Our current approach leads to a high degree of bias, resistance, and failure as we promote changes that challenge Another’s status quo. We don’t realize that anything ‘new’ must fit with the status quo or it gets rejected. We don’t realize we’re actually causing the resistance we receive.
And resist they do – not because our data or goals aren’t worthy or necessary, and not because they don’t want to change per se, but because our good will, shared information, and ‘push’ tactics conflict with the Other’s unconscious system that protects itself from unknowable disruption.
Indeed, any modifications to the status quo would have to be performed in a way would leave the system congruent. And the time it takes for the system to accept and make room for the ‘new’ is the length of time it takes for adoption. With the best will in the world our suggestions challenge their Systems Congruence.
And unfortunately, as doctors and sellers, trainers and consultants, parents and coaches – as influencers – we don’t have the skills to do more than attempt to cause the change WE think is needed, rather than elicit it. We don’t naturally possess the skills of Servant Leadership.
GIVE UP INDIVIDUAL NEEDS
True Servant Leadership enables others to elicit their own congruent change. We need new skills that facilitate Others, and a switch in perspective to enabling Others to discover their own answers by facilitating Another’s change, offering real leadership.
I’ve spent my life coding and training the unconscious route through to choice and change to enable Others to discover their own Excellence, an Excellence that complies with their own Beliefs, an Excellence that can be eagerly, joyously adopted because it operates from within their status quo.
Servant Leadership assumes:
- Others have their own answers and are the only ones who can effect their own change. An outsider (regardless of intent, need, or efficacy of message) can never, ever, fully understand the inner workings of Another’s unconscious system. Our responsibility is to lead them through the pathway to change themselves.
- We only have questions for Another, not answers. And since conventional questions are biased interrogations (biased by the wording, the intent, and the goal of the Asker) that may miss important, hidden, elements necessary for the Other to elicit their change criteria, I’ve designed a new form of question (Facilitative Questions) that lead Others through their own trajectory of change to discover their own answers, in a way that causes new understanding and decision making.
- There is no way for an outsider to have THE ANSWERS for Another. They have no knowledge of the Beliefs or the systemic elements that created and maintain the problem and that must buy-in to any change.
- To listen without bias or misunderstanding, we must practice Dissociative Listening to avoid the filters, bias, assumptions, and triggers that are part of our normal listening. [Note: for those interested in learning Dissociative Listening, read Chapter 6 in What?.]
Decades ago, I mapped the sequential steps of systemic choice, change, and decision making enabling people to discover their own best choices that match the rules and values of their internal system. These steps traverse a pathway from the unconscious through to buy-in and Systems Congruence so change is comfortably adopted.
I have taught these skill sets to influencers in business, coaching, leadership, and healthcare to assist in facilitating permanent, congruent change: to help buyers buy, to help coaches, leaders, and doctors elicit congruent, permanent change, to help learners learn permanently – eliciting the core of the unconscious HOW to facilitate Another’s excellence their own way – to find their own answers.
So what would you need to know or believe differently to be willing to begin interactions as a Servant Leader rather than a coach, parent, seller, leader? How can you know, given the skill sets and foundations are so different, that it’s worth taking the time to add new skill sets to the ones you already use? Imagine having the skills that truly enable Others to find their own Excellence. Imagine being a true Servant Leader.
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen April 17th, 2023
Posted In: Listening
The Discipline of Listening
 Our brains make it difficult, if not impossible, to fully or accurately comprehend what our Communication Partners wish to convey. Entering through our ears and traveling through our neural pathways in five one-hundredths of a second, incoming sound vibrations get deleted, filtered out, and sent to ‘similar enough’ circuits for translation, not necessarily matching what the Speaker intended. And because our brain doesn’t tell us what it deleted or misinterpreted, what we end up thinking we’ve heard may be an altered rendition of what was said.
Our brains make it difficult, if not impossible, to fully or accurately comprehend what our Communication Partners wish to convey. Entering through our ears and traveling through our neural pathways in five one-hundredths of a second, incoming sound vibrations get deleted, filtered out, and sent to ‘similar enough’ circuits for translation, not necessarily matching what the Speaker intended. And because our brain doesn’t tell us what it deleted or misinterpreted, what we end up thinking we’ve heard may be an altered rendition of what was said.
I spent 3 years researching and writing on this topic for a book, (What?) and came away in awe of the magnitude of this issue and how deeply our neurology prejudices our conversations, and how much of what we think we hear someone say is inaccurate.
THE PROBLEM WITH GOAL-CENTERED LISTENING
When we listen for something specific, the problem is compounded: we often take away a myth as meaning. As a coach to coaches, sellers, and managers, I’m painfully aware of how sellers often listen only to “recognize a need“, or coaches listen for a problem they’ve had success resolving before, or managers listen for a difficulty they know how to regulate.
The very act of listening for something specific causes a further diminution of real understanding, providing some unknown percentage of accurate data with which to base follow-on decisions, not to mention that everyone potentially walks away from the conversation with mistaken beliefs, feelings, and expectations. And then we blame the Other for any failure.
Sadly, because our brains don’t tell us they have misunderstood or biased what was said (we have no reason but to believe we’ve “heard” accurately), we’re rarely aware that we have missed the meaning or the possibility until it’s too late.
TIPS TO LISTEN ACCURATELY
Here are some questions to think about as you consider adding some discipline to your listening skills:
- Prepare and De-stress. Before each conversation, clear your mind of any expectations or hopes, or feelings from past conversations. Otherwise your brain will unconsciously seek confirmation (Confirmation Bias) for that very thing while ignoring or misconstruing possibilities (minimizing your chances of success or creativity).
- Humility and humor. Unless you have written a script that everyone speaking has signed off on, you have no way of knowing what your Communication Partner will say, mean, need, or feel. I often hear people attempt to push their own agenda and don’t recognize what the Other has conveyed. Since there is no such thing as win/lose, this tends to create lose/lose, although the offended Communication Partner might not mention it during the conversation.
- Flexibility. All conversations demand flexibility to be present to the messages within the dialogue that actually occurs. The larger the bias or expectation going in, the harder it is to achieve, the greater the gap in understanding and expectation, and the greater the fallout from unrealized possibility.
- Trust. I know it’s hard to walk away without getting exactly what you want, or to hear things that don’t match your needs or expectations, but somewhere in the conversation there is a creative win for everyone. It may not look or act like your dream, but it will be something that everyone can accept. Besides, if you’re not trusting the dialogue actually occurring, you’re merely pushing your own agenda. And then you can’t even trust the outcome you’ve devised.
Unless both sides of a conversation fully understand what the Other intends to convey, there is no reality to work with and everyone risks unnecessary failure or limited possibility: it might have been possible to achieve success in a different way, or maintain a relationship over time for future possibilities. In almost every in-person coaching session I have had, my client has missed real possibilities (even of getting exactly what they want) in pursuit of hearing what they believe they should hear.
Here are some questions to think about as you consider adding some discipline to your listening skills:
- How adept are you at entering conversations with no needs, no expectations, no biases?
- How capable are you of showing up in a conversation with the ability to have a We Space – not two “I’s” which lead nowhere except self-serving exchanges, but a genuine melding of the people involved to find the win for all?
- What do you need to believe differently to recognize that when you enter conversations with personal biases, assumptions, and triggers, that you will only succeed those times when the Other has the exact same biases, assumptions, and triggers – and all those who could truly benefit from your expertise and heart will not be able to hear you either (regardless of how well-meaning or accurate you are)?
- How willing are you to learn to show up with an open mind, recognize when you have biases or expectations and quiet them before starting the exchange?
- How can you react to something you’re not prepared for in a way that encourages collaborative dialogue?
You can continue doing what you’ve been doing, of course. But for those times you seek excellence in your conversations, a bit of preparation is in order.
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen April 10th, 2023
Posted In: Listening
Steps Along the Buying Decision Path
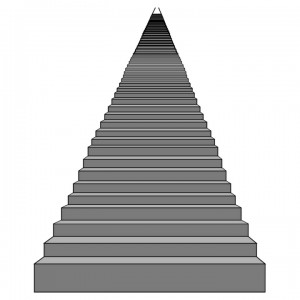
As s ellers we are taught to find prospects with a need that matches our solution and then find creative, professional ways to pitch, present, entice, push, market, or somehow introduce our solution to enable them to understand how our solutions will fix their problem.
ellers we are taught to find prospects with a need that matches our solution and then find creative, professional ways to pitch, present, entice, push, market, or somehow introduce our solution to enable them to understand how our solutions will fix their problem.
Unfortunately, we fail to close over 95% of the time (from first contact) regardless of how well their need matches our solution. And it’s not because of our solutions, our presentations/pitches, or our professionalism. It’s because the sales model does not include the skills to facilitate the largest component of buying decisions – those systemic, idiosyncratic, behind-the-scenes, change management decisions that comprise their Pre-Sales processes, exclude outsiders, and have absolutely nothing whatsoever to do with buying anything.
Until they go through this process and walk through each stage of managing their unique change management issues, until everyone who touches the final solution agrees to a change, until the entire team is assembled and lends their voice to ideas, problems, solutions, and fallout, they cannot buy regardless of how much they may need our solution. They must do this – with us, or without us. It takes much longer without us, hence a protracted buying decision and closed sale. Without appropriate change management, they cannot buy. And the sales model doesn’t address this, causing sellers to spend most of their time finding ways to get in – and missing the route in because of their focus on solution placement. The route is change management.
FACILITATING CHANGE IS NOT SELLING
I’ve spent the last few decades coding and designing new tools to promote buyer readiness and help sellers facilitate buyers through their Pre-Sales decision path that buyers go through without us and is not focused on buying/solution choice. My model, called Buying Facilitation®, gives sellers the tools to be Facilitation/Change Consultants to get onto their Buying Decision Team, facilitate their change-management decisions, lessen the time between decision making/close, and differentiate from the competition. It’s a model that works with sales, but focused on enabling our buyers to congruently manage their systemic change, which has always been done outside of our purview until now.
Here’s the question to ask yourself: do you want to sell? Or have someone buy? They are two different activities, necessitating two distinct skill sets. Sales merely handles one of them. Buying Facilitation® works with sales to first help buyers manage their consensus and change issues to ready them to buy.
Using Buying Facilitation® first, then sales, will immediately enlist those who can buy, and immediately get rid of those who will never buy. After all, we all know too well that when buyers buy there doesn’t seem to be a direct line between their need or the relevance of our solution: it’s about their ability to manage their environment to make the necessary decisions that will lead them to congruent change and to their best possible outcome – which may, or may not, be to buy anything. When we speak with prospects to discuss need, we have no idea if the information we’re being given is the takeaway from all assembled voices, if the group has already agreed to buy anything, or what stage of the decision path they’re on. Are they merely gathering data for options? To bring back to the team? To compare with competitors?
Here are the steps I’ve discovered that buyers – all change – must address. As you read them, note that facilitating change is not sales, and includes some unique skill sets, goals, and outcomes.
1. Idea stage. Someone has an idea that something needs to change and discusses his idea with colleagues.
2. Assembly stage. Colleagues meet and discuss the problem, bring ideas from online research, consider who to include, possible fixes, and fallout. Groups formed.
3. Consideration stage. Group meets to discuss findings: how to fix the problem with known resources, whether to create a workaround using internal fixes or seek an external solution. Discuss the type/amount of fallout from each.
4. Organization stage. Organizer apportions responsibilities, or hands over to others.
5. Change Management stage. Meeting to discuss options and fallout. Determine
a. if more research is necessary (and who will do it),
b. if all appropriate people are involved (and who to include),
c. if all elements of the problem and solution are included (and what to add),
d. the level of disruption and change to address depending on type of solution chosen (and how to manage change),
e. the pros/cons of external solution vs current vendor vs workaround.
f. possible workaround and if they are sufficient.
6. Addition stage. Add needs, ideas, issues of new members; incorporate change considerations.
7. Research and change stage. Everyone researches their portion of the solution fix (online research—webinars, etc., call current vendors or new vendors etc.). Discussions include managing resultant change.
8. Consensus stage. Buying Decision Team members meet to share research and determine the type of solution, fallout, possibilities, problems, considerations in re management, policies, job descriptions, HR issues, etc. Buy-in and consensus necessary.
9. Choice stage. Action responsibilities apportioned including discussions/meetings with people, companies, teams who might provide solutions.
10. Meet to discuss choices and the fallout/ benefits of each. Discuss different solutions and vendors.
11. Vendor/solution selection. Meet with possible vendors.
12. New solution chosen. Change management issues incorporated with solution choice.
13. New solution implemented.
The sales model handles steps 10-13. Marketing, marketing automation, and social marketing may be involved in steps 3 and 8, although it’s not clear then if the decision to choose an external solution has been made, the full fact pattern of ‘needs’ has been determined, what the marketing content is being used for, or if the appropriate decision makers and influencers are included. Buyers muddle through this but we can enter earlier and help them transition through their steps, so long as we stick to our initial roles as facilitators and not try to sell or manipulate.
BUYING FACILITATION® IN ACTION
I started up a tech company in London 1983-89 and developed Buying Facilitation® to teach my sales folks to navigate buyers through their decision path, change management, and buy-in BEFORE they began selling. We increased sales 5x within a month. I’ve been teaching this model in sales and coaching to global corporations since 1989 with similar results.
My book Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell discusses these steps and how Buying Facilitation® can work with sales and marketing to enter the buy path earlier, and to help coaches, leaders, and negotiators facilitate congruent change. It’s truly a change management skill that makes a seller a real consultant and uses entirely unique change facilitation skills: Facilitative Questions, Listening for Systems, and Choice. Remember, needs/solutions are irrelevant until buyers understand how any change will affect their status quo. The sales model isn’t designed to handle this Pre-Sales change management function. Read the book 🙂
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen March 27th, 2023
Posted In: News
The Cost of Automating Customer Care
 Remember when a person would answer a company phone? I found myself shocked recently when a live human answered. “Um, Hello?? Are you a real person?”
Remember when a person would answer a company phone? I found myself shocked recently when a live human answered. “Um, Hello?? Are you a real person?”
When we call a company these days we often get caught in one of those automated loops that lead us from one wrong person to another, from one long hold to another, ultimately landing us where we started, with no resolution, lots of frustration, and rage toward the company. Company websites aren’t any better: no way to connect except via links that either lead nowhere or never get responded to; chat bots that have no idea what you’re talking about and keep repeating perky phrases.
As a paying support customer, I once waited 13 hours for a promised ‘one-hour’ call-back from Best Buy to resolve an urgent technical problem. I went to sleep with the phone in my hand, waiting. When the call came at 3:00 A.M. (!) the tech started by asking me how I was. “I’m sleeping! It’s 3:00 in the morning and I’ve been waiting since 2:00 in the afternoon! And I still have my technical problem!” And he hung up on me. This was particularly egregious given I’d been forced to listen (for hours!) to Best Buy’s ‘hold’ jingle promoting fabulous customer service.
We’ve all learned to accept these indignities, to be ignored if we have a problem, to spend hours attempting to resolve a crisis caused by our purchase. And it’s getting worse.
CUSTOMERS DON’T SEEM TO MATTER
We’ve grown to hate our providers, and they don’t seem to care. But they should. We provide the income for their profit and salaries, certainly enough to hire employees to answer phones or help solve problems. In so many ways, hiring a human would be cheaper than the cost of the automation.
Gone are the days when customer service mattered, when three rings was the maximum number before phones had to be answered to keep customers from being frustrated. That doesn’t seem to matter anymore.
Companies now use only two criteria to interact with customers: Time and Cost. And because these companies may be sole providers in regional sectors or global behemoths, users have no choice but to remain customers.
Sadly, there’s no regulation on this, no way to reduce our monthly payment by the number of hours we spend on hold, or the number of problems we can’t get resolved. Until we form a Citizen’s Council, or there’s some sort of regulation – neither of which are likely – we’ll just have to suck it up. Nobody cares, no one is responsible, and no one pays for the problem except us.
What happened? How did our companies go from touting stellar customer service as a competitive advantage to computerizing all human interactions? How did companies decide to stop respecting the very people who keep them successful? Why have they been so willing to cause their customers to distrust them?
POSSIBLE CAUSES
We know what companies pay their ‘C’ level people, their profit margins and how much they pay (or not) in taxes. We know they can afford to hire customer support folks. But somewhere along the way customers became secondary. What’s going on? Is greed the only motivation these days? How did it become a ‘thing’ that customers don’t matter – except for their purchases?
Frankly, I have no way to think about this in an unbiased way. I’ve spent my life developing facilitation models that enable win/win and servant leadership, to respect each individual and engender trust. Making it difficult for the very folks you depend on to get the service they require goes against all my beliefs.
It might come from the momentum of ‘cheap’. Everything seems to require a low price tag, and money becomes the main criteria for choice. We don’t consider what happens when goods are reduced to a price tag, for doing ‘whatever it takes’ for price to be the sole choice criteria. We avert our eyes when we learn that companies use children as cheap labor or when they strip the environment to create cheap products.
We seem to want cheap even when price differentials convey value differentials. Someone once asked the price of my Buying Facilitation® training, a unique model I invented that uses mindbrain connections to help buyers generate their buying decisions. When I told him the price (thousands) he told me he could get ‘almost the same’ course at ATT for $49. I told him to take it 😊
Are we all implicated here? Is automated customer service the fallout from the search for cheap? How did we move away from scrupulous business practices, or good customer care as a competitive advantage? Why isn’t it a simple calculation that happy customers provide more revenue?
Somewhere in the past few years automation became the accepted corporate interface regardless of the toll on customers. And I can’t imagine that focus groups would chose automation and no-human-contact as a preference over being cared for by a human.
BEST PRACTICES
I have some ideas that might stop this nonsense. My favorite is that each call is answered by a representative who owns the problem to its conclusion. I suspect that when companies pay their own folks to sit on hold for hours only to get connected to the wrong department, they just might fix the problems. They don’t seem to respect a customer’s wasted time; maybe they might care when it’s their own time.
Here are my ideas:
- Human beings will pick up customer service lines; site links will go to real support people who will respond within 12 hours.
- The person who picks up the phone will own the problem.
- Customer Care will be seen as a competitive advantage.
- Companies will pay bonuses to reps who keep customers happy.
- A vehicle – a YouTube Channel, for example – specifically for customers’ complaints. Their grievance gets calculated as a cost to the company, with a running tally of how much money the company owes its customers. At the end of a month the company gets sent a Grievance Bill with the proceeds going to charity.
- An advertised day a month of “no shopping” in the companies who don’t serve customers adequately.
Sadly, the very people who sell us services have become adversaries. What do we need to do or say to have our needs met, our voices heard, our time respected? What do companies need to know, believe, or do differently to be willing to provide resources to handle incoming calls, or provide websites that offer support? What can any of us do to knock some sense into their heads?
Does anyone have better ideas that might help? God knows, I don’t.
________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen March 13th, 2023
Posted In: Communication, Listening
Can We Know When We Don’t Know What We Don’t Know?
 Years ago I visited a spa where 4 magnificent macaws stood on individual perches, each with a long, not necessarily heavy, chain around one of its legs. Yet the chains were not attached to anything: if the birds had known what they didn’t know, they could have easily flown away.
Years ago I visited a spa where 4 magnificent macaws stood on individual perches, each with a long, not necessarily heavy, chain around one of its legs. Yet the chains were not attached to anything: if the birds had known what they didn’t know, they could have easily flown away.
I was reminded of that recently when sitting with a close friend starting up a company. I suggested he write down 1. What he knew he knew; 2. What he knew he didn’t know; 3. What he didn’t know he didn’t know (This being impossible, but the column needed to be there as you’ll see.). A long-time friend, James was always up for my mischief. He promptly began writing a list of what he knew that he knew. As I looked on, knowing him as long as I did, I noticed two items I knew for certain he did NOT know.
I told him I had doubts about some of the items he thought he knew and that they belonged in the ‘don’t know that I don’t know’ column. I asked him how he’d know if thought he knew something but in fact was mistaken.
“Oh. I guess there’s no way to know unless I fail. Without knowing there’s any other option, I wouldn’t even know when I need help or the kind of help I needed.”
A similar situation came up recently when a colleague explained how his sales team ‘truly cared’, and ‘truly served’ prospects. When I asked him what skills he was using to care and serve, he rattled off the same skills he used when selling. And even though we’d known each other for some time and he’d read a couple of my books, it never occurred to him to contact me to learn additional skills he knew I’d developed specifically for what he was doing. Why? Because his results were ‘wildly successful’ – a close rate ‘higher than others’ (10% success vs 5% industry standard – but still a 90% failure). He never stopped to consider that he could have been much more successful with additional skills. He didn’t know what he didn’t know.
OUR BRAIN
So how do we know when we don’t know what we don’t know? We don’t even know how to think or consider something outside our assumptions or beliefs, or something not already in our neural makeup. There’s just no way to know what outcomes, risks or rewards, skills, comparators, or thought processes are possible. So how do we attain the courage to do something different when we have no way to even think about it?
Let’s consider how we do anything at all. Our brain instigates our actions, thoughts, what we hear, how we decide and choose, how we behave. When we have an idea or goal, hear a lecture or are given a directive, our brain
- receives and filters (some deletion involved) incoming vibrations – words being meaningless puffs of air until our brain translates them – and
- turns them into electrochemical signals that
- get sent down well-worn pathways (superhighways) that
- lead to existing, ‘similar-enough’ circuits (some deletion involved) that
- instigate habitual behaviors and outcomes.
In other words, whatever we think, hear or read enters our mind as sound vibrations that end up being (mis)translated through some conglomeration of synapses, pathways, circuits, etc. and we end up ‘hearing’ little more than something we have previously experienced, regardless of the facts. And our brain doesn’t tell us what havoc it’s played: we just assume what we think we heard is accurate.
I was once meeting with a couple who were licensing some of my material. I made a comment that John interpreted what I said as X when I actually said Y. I carefully explained, again, what I’d said. Here is what followed:
John: You didn’t say that! I heard you say X with my own ears!
SD: No, John. You misheard. I said Y.
Wife: John – she really said Y. I was standing right here. You heard her wrong.
John: YOU’RE BOTH LYING!
And he stomped out of the room, and never spoke to me again.
Listening is a brain thing, causing us to interpret incoming sound vibrations according to where among our 100 trillion neural circuits the sound vibrations get sent. [See my book What? Did you really say what I think I heard?] Indeed, we hear some rendition of what a Speaker means to say, and rarely ‘hear’ accurately. Let me explain.
The way our brain turns signals into behaviors, ideas, or thoughts, determines everything we hear, think, and do. Usually it’s a good thing. It’s how we know to get up in the morning, put our slippers on, and brush our teeth. It’s how we make our decisions, go on our diets, make our New Year’s resolution. But it’s restrictive. In fact, and I still get annoyed about this, our brains automatically pretty much keep us doing what we’ve always done and we have very little say in the matter.
Indeed, we live our lives restricted and directed by how our neural circuits translate for us. And certainly, that provides a lifetime’s worth of choices. But: our curiosity, our ideas, are restricted by what’s already there.
I’ve developed a model to make it possible to change habits and behaviors by consciously adjusting your unconscious hierarchies and neural pathways. It includes wholly new skills, tools, and thought process with a hands-on learning and Belief change process.
Can we know what we don’t know that we don’t know? Because when we can’t, we’re left with the results of fewer choices with no way to know what to look for if we need to add something new.
WHAT’S IN THE WAY OF ENCOURAGING ‘NOT KNOWING’
Don’t get me wrong. none of us ever intends to mishear, or misunderstand, or restrict ourselves. But we’re basically out of choice, never told what our brain has edited or deleted, or what other choices were possible if our brain chose different circuits to translate the incoming vibrations.
Let me share my thoughts on some of the reasons I think people have a hard time getting beyond what they know (or don’t know they don’t know):
- Ego. People have a hard time acknowledging they are ‘deficient’. I’m not sure why. My question is: “What would stop you from seeking assistance at those times you’re aware that you are missing knowledge? Those times you have a pattern of failing and have no additional options?”
- Assumptions. When we presume we know something, we have no reason to think differently. Unfortunately, when failure occurs we have a ‘blame’ response since we, obviously, can’t be wrong and the Other, obviously, must be the culprit. Entire fields are based on Others being wrong because they don’t heed the provider (healthcare, sales, coaching, etc.).
- Denial. Wrong? I’m not doing anything wrong. Better? I already know how to do that. I really don’t want to change. I know my stuff is better. Why should I want to know what I don’t know when I already know what’s best? Sometimes people prefer their own ideas and ignore incoming content that would lead them to greater success.
- Listening Bias. Sometimes we are so committed to a specific outcome and approach that we consider successful that we listen to others through very biased ears and allow our brain to tell us what we want to hear…without question. I try to avoid this by seeking answers from people from different industries, or countries. But when we enter a situation with the end in mind, whatever we hear, whatever we take away, will be biased by our history.
- Fixed Views. We become attached – both emotionally and neurologically – to what we know. With a habituated superhighway that leads us straight to oft-used answers and beliefs, we dislike going through the decoupling process to accept and adopt a new answer.
Net net, due to our lazy brain and idiosyncratic personalities, there’s no way to naturally recognize when we don’t know what we don’t know. This makes it quite difficult to learn anything new until we fail and it becomes obvious.
HINTS
Here are a few ideas that might lead to more choice:
- When you face confusion, it’s because your brain’s dispatch unit (the Central Executive Network) can’t find an existing set of circuits to translate or interpret new ideas – a perfect time to recognize there’s something you don’t know.
- When you’ve had repeated failure, there’s something you’re missing. What needs to happen for you to get curious? Assume there are better answers somewhere?
- Ask others who know more than you do. Here is where a good friend or coach comes in. People who are outside your field will ask questions that you may not have answers to. And you need to find them!
- Research. When I’m developing a new model I do broad research – reading sample chapters or whole books on unfamiliar topics (Picking Up by Robert Nagle about the New York City garbage collection provided new ideas about systems), researching papers and articles on topics adjacent to my ideas – to find new concepts that I hadn’t heard before to stimulate further thinking. I’ll never forget how my world shook when I learned that no input (no ideas, words, sounds) could be interpreted outside the circuits I have in my brain already. That upset me for a week! And it absolutely shifted my thinking.
Entire fields are missing information and doing nothing to discover what they don’t know:
- Healthcare professionals don’t know why patients ignore their directives. For instance, handing someone a new food plan without them knowing how to change habits and neural circuits congruently will instigate resistance. Instead of doctors blaming themselves for not knowing how to facilitate congruent change, they blame patients for not having motivation.
- Coaches, managers, leaders, supervisors assume their mandates will be followed. Clients who don’t follow them are said to ‘not really want to change.’ At no point do they acknowledge that their approach may be the problem.
- Sellers and marketers continue to push solutions, overlooking the way people actually buy and face lower and lower success rates (now 5% rate) that should alert them there’s something they don’t know. What other industry believes that a 95% failure rate is ‘success’?
- The training model fails 80% of the time. Pushing new content into a brain that might not have circuits to translate it accurately causes confusion, resistance, and disregard causing trainers to assume learners are ‘unmotivated’. Learning how to design programs that generate wholly new circuits for the new knowledge is not anything instructional designers know they need to know.
- Business Process Management uses a flow chart that invites front line workers into the process halfway through the flow! Obviously this leads to implementation problems, such as insufficient data collection and resistance when people are pushed to be compliant against their will. One of the leaders in BPM recently approached me about adding the Steps of Change (a model I invented that facilitates the flow of change and decision making) to help them, but he became agitated when I suggested he needed to begin at Step One by assembling everyone who touches the problem. He left our discussions, not realizing he was following the exact failed format he called me to change.
- OD and Change management relies on standard questions which are biased and restricted by the thoughts of the asker – and ignore the foundational Beliefs and norms that shift in the Other’s brain for congruent change to occur. And they don’t question why they get resistance, time delays, lack of buy-in. They just blame the Other.
So I leave you with these questions:
– How committed are you to having the full set of data you need for success?
– How willing are you to forego your ego and Not Know?
– What would you need to know or believe differently to recognize when you don’t possess the full data set you need?
Imagine how successful we could all be if we knew what we didn’t know and had the right attitude to find out.
___________________________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com.
Sharon Drew Morgen February 6th, 2023
Posted In: News
Facilitative Questions: Questions that facilitate change
There’s a universal assumption that well-crafted questions will result in ‘good’ responses. But as leaders, coaches, sellers, and search-developers know, that’s not necessarily true.
Sometimes questions end up gathering incomplete or flawed data. Or the questions unwittingly cause resistance because they’re not interpreted by the Responder as we intend. Or they are worded in a way that’s biased by the Asker’s unconscious beliefs and miss better answers that would lead to different, possibly better outcomes.
WHAT ARE QUESTIONS AND WHAT DO THEY DO?
Have you ever wondered why the questions we use often don’t achieve what we want them to achieve? Here’s why:
- Conventional questions seek to extract information. But due to the unique word choices and specific goals of the Asker, they can miss the real answer that’s sometimes lodged within a Responder’s unconscious, or the LLM’s database, and outside the scope of the question posed.
- Conventional, or information-based, questions are biased: by the Asker seeking or assuming a specific type of response; by the Responder whose responses are dictated by the biases and assumptions within in the question.
Conventional questions – even those we ask ourselves! – are great for simple queries, but may not uncover good answers. After decades of brain research, systems thinking, and figuring out the gap between what’s said and what’s heard (Read my book WHAT?) I’ve discovered a way to formulate questions that finds the precise neural circuitry where accurate answers are stored.
What if it were possible to formulate a question that would:
- extract accurate data,
- influence change,
- promote efficient implementations, buy-in, and sales cycles,
- avoid resistance and bias, maintain personal integrity,
- act as a filter and conductor for good decision making,
- facilitate permanent learning and habit change,
- help Responders (buyers, clients, patients) and search Users discover the unconscious criteria that evoke accurate answers?
Certainly it’s quite possible to pose good questions. But sometimes conventional questions lead to inadequate, biased, or reactive responses.
I suggest it’s possible to use questions in a way enables Responders to discover their own answers based on their own unique beliefs and mental models, reducing inaccuracies and reactions, and making real change and decision making possible.
INFLUENCING CHOICE
My life’s work involves studying the brain for ways to impact unconscious choices, with a focus on unbiased ways into the brain to help people uncover their own answers and generate new choice.
In other words, in addition to helping us discover ways to change personal habits or make good decisions, coaches could lead clients to where their best answers are stored; sellers could facilitate buyers through to decision making without bias; search could prompt the right questions to summon the best answer.
In 1988 I read Roger Schank’s The Creative Attitude that discusses how our brains store data in memory that can only be discovered by using exact words that get sent to the exact brain circuitry where they’re stored. Interesting, I thought. But how is it possible to get to specific brain circuits?
I already knew that we unwittingly listen through biased ears due to the way brains process and dispatch incoming sound vibrations. Was it possible to use questions to unlock the unconscious drivers, the beliefs, the values, the emotions at the core of all decisions? Could questions be formulated in a way that gets to the exact part of someone’s brain where their answers were stored amidst their 100 trillion neural connections?
Using my knowledge of the mind->brain connection I began experimenting with new forms of questions that would avoid bias altogether. It took me 10 years to break down the elements necessary. I eventually developed a new form of question (Facilitative Questions) that eschews information-gathering, and instead leads Asker’s to the exact brain circuits – congruent with their values and beliefs – to facilitate their accurate unconscious choices, unbiased by wording or intent, for personal decisions and change.
THE PROBLEM WITH INFORMATION
Conventional questions seek information as per the needs of the Asker. They cause retrieval, translation, and relevance issues in the Responder:
- We each translate incoming words (called puffs of air by neuroscientists) according to our mental models, beliefs, history, and existing neural circuits, causing misinterpretations and misunderstandings that may be quite different from the intent of the Asker, producing unintended reactions and responses.
- Because of the way our brains uniquely hear and interpret incoming words, incoming information may be misinterpreted, potentially affecting people’s beliefs negatively, regardless of the intent of the Asker.
- Real answers are unique and held in Long Term neural circuitry within a Responder’s brain, sometimes stored in ways that aren’t conscious or easily accessed.
- We can only hear, see, feel, think, notice, etc. what exists in our neural circuits, causing each of us to live in worlds biased and restricted by our histories. It’s the same with current AI, which restricts responses to the way it interprets questions – not necessarily as intended by the asker – and captures and shares content accordingly.
With a data elicitation focus, conventional questions often cause failure:
- Sellers gather information to ‘recognize’ a buyer with a ‘need’ they can pitch to – often leading to false assumptions and interpretations by the seller – when they can use the same time to actually find and lead prospective buyers through their decision making steps based on their own criteria and avoid rejection;
- Coaches, consultants, facilitators and leaders pose questions biased by their assumptions and desire to influence. To that end, they risk causing resistance and certainly miss the opportunity to direct the Other’s brains to where their own answers are stored, eschewing resistance and enabling permanent change along the way.
- Change Management professionals generate their goals, processes and implementations when gathering incomplete data from only a subset of folks involved in the initiating problem, causing resistance, delays, and failed outcomes when asked to apply the new activities.
- Search queries are reduced to how LLMs interpret them, often in a manner biased by the search engine or AI, and often missing the real intent of the User. It’s possible to lead users to their specific circuitry to guide search to the most appropriate response.
- Decision analysts and tech developers use their own biased curiosity to gather, weight, and analyze needed data, potentially extracting incomplete or inaccurate information when it’s possible to evoke accurate answers by formulating differently worded questions.
Eventually I invented a wholly new form of question that gets to the exact neural circuits where accurate, values-based answers are stored.
FACILITATIVE QUESTIONS
Facilitative Questions (FQs) are brain-directional and go to specific parts of the brain that will capture the appropriate, most relevant, unconscious content from a Responder’s memory or LLM’s database.
Facilitative Questions differ from conventional questions in their intent and scope. They are brain-directional and don’t seek information, but formulated in a way that mirrors how brains process, store and retrieve personal, unconscious, belief-based and historic data from a Responder’s memory – great for making complex personal decisions, buy-in, and for making habit and behavioral changes; great for helping search capture the most appropriate content that matches the real, often unconscious needs of a User.
Using specific wording and sequencing, FQs shift the onus of responsibility from the Asker wanting answers to enabling Responders and AI to find and generate answers based on their history, norms, beliefs, and mental models. In other words, influencers – (sellers, coaches, therapists, friends, clients – even search engines!) become facilitators who enable Others to discover their own Excellence, with no guesswork or resistance.
But they are complex, outside conventional thinking, and can’t be formulated without additional learning. [If you’re interested in learning how to formulate them, get the Learning Accelerator or my MP3 series where I use, role play, and explain them for sales, coaching, and fundraising.] Without using precise wording or sequencing, without enabling Responders to listen from a Meta position, FQs become highly manipulative, fail to retrieve important ideas or information, and miss an opportunity to enable Others to change.
Facilitative Questions:
- use specific words in a specific order to reach the specific place in the brain that stores the best answers;
- put the Responder into Observer/coach/witness to reduce any natural biases and expand brain search;
- open new choices within the unconscious of the Responder to make it possible to fix discover their own excellence;
- construct new awareness, new choices, new behaviors based on unconscious belief/values-based criteria;
- are non-manipulative and non-biased;
- offer change agents a new skill to engage the right people, address the right problem, and manage change without resistance;
- eschew information gathering;
- eliminate resistance by eliciting commitment and buy-in at the very beginning of any project or initiative;
- enable Responders to simultaneously uncover the unconscious core of the problem and create the necessary change on their own.
Here’s a very simple example of the differences between conventional questions and Facilitative Questions:
Information-based question (conventional question based on the goals, word choices, word usage of the Asker): Why do you wear your hair like that? This question is an information gathering question based on the needs of the Asker and capture oft-used, habitual, automatic responses. Also, all ‘why’ questions cause a Responder to defend current choices and underlying beliefs. If a question invades the Responder’s beliefs, the response will be biased and resistive. There’s a good chance a conventional question would gather incomplete or inaccurate data.
Facilitative Question (sequential navigational question that directs Responders to the exact brain circuitry where their unconscious information is stored): How would you know if it were time to reconsider your hairstyle? This question begins by putting the Responder into a Meta position to have an unbiased, broader expanse of their neural circuits to peruse for answers, and uses words in the order that brains can dispatch them to the proper circuits. With no intent to capture information, with no bias or manipulation, the Asker becomes the facilitator/change agent/servant leader.These cause no resistance. Specifically:
- users of search and AI can find their best answers with less guesswork and minimal bias;
- buyers can recognize issues that would help them make decisions, assemble the right people, and instigate buy-in to ready them to buy;
- coaching clients can be led to they’d need to address for permanent change and eschew resistance;
- doctors can elicit natural, permanent behavioral change in patients rather than push to try to cause change, etc.
By helping Others discover their own criteria for change and decision making, by enabling search to efficiently find accurate responses, by finding accurate answers for researchers and influencers, Facilitative Questions provide an expanded scope to cull accurate answers and increase the probability of quality responses.
FACILITATING CHANGE
The big idea here is the change in the intent of the questions: FQs are brain directional. They trust that accurate answers are stored in unique places in brains that may not respond to conventional questions that are biased by the needs and wording of an Asker. After all, there really is no way for an outsider to ever know the full extent – the connections, history, values, complications, etc. – of how someone’s internal system is set up. The differences are important:
- from seeking and pushing content to achieve the influencer’s goals to facilitating the person’s own discovery of beliefs, values, identity issues and systemic drivers, and eliciting (not causing) change;
- from guessing at answers based on an algorithm or an Asker’s needs and beliefs to enabling the discovery based on a Responder’s unique criteria;
- from bias and resistance to participation and creativity;
- from directing change and creating resistance to discovery, buy-in and participation.
To use Facilitative Questions requires a different sort of thinking and a different level of control. Most of all it requires that influencers change their goal to truly serve the other, to help Others initiate and manage change from within – not with any content or directive from the Asker, but true buy-in.
What would you need to know or believe differently to be willing to add a new questioning technique to your already superb questioning skills? How would you know that adding a new skill set would be worth the time/effort/cost to make you – and your clients – even more successful?
____________
Sharon-Drew Morgen is a breakthrough innovator and original thinker, having developed new paradigms in sales (inventor Buying Facilitation®, listening/communication (What? Did you really say what I think I heard?), change management (The How of Change™), coaching, and leadership. She is the author of several books, including the NYTimes Business Bestseller Selling with Integrity and Dirty Little Secrets: why buyers can’t buy and sellers can’t sell). Sharon-Drew coaches and consults with companies seeking out of the box remedies for congruent, servant-leader-based change in leadership, healthcare, and sales. Her award-winning blog carries original articles with new thinking, weekly. www.sharon-drew.com She can be reached at sharondrew@sharondrewmorgen.com
Sharon Drew Morgen February 5th, 2023
Posted In: News


